A brand new examine has used highly effective imaging to disclose a subset of Alzheimer’s-associated proteins spreading notably quickly. These ‘superspreaders’ might assist clarify why irregular clumps of the naturally occurring amyloid beta proteins improve because the debilitating illness progresses.
“This work brings us one other step nearer to higher understanding how these proteins unfold in mind tissue of Alzheimer’s illness,” explains molecular physicist Peter Nirmalraj from the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Supplies Science and Expertise (EMPA).
Prying the direct explanation for Alzheimer’s neurological injury from the chaotic molecular tangles in our brains has to date confirmed extraordinarily tough. Whether or not amyloid beta plaques are a trigger or a symptom of the illness can be nonetheless up for debate.
Laboratory research have discovered no proof these proteins straight injury mind cells, and coverings geared toward these proteins have not confirmed efficient.
Analysis printed this yr means that whereas the plaques themselves might circuitously trigger neuron injury, different molecules that get tousled with them could also be accountable. Regardless, understanding the mechanisms behind the overgrowth of amyloid beta proteins should result in higher therapies.
Of their new examine, Nirmalraj and colleagues from the College of Limerick in Eire used highly effective new methods to look at how amyloid beta proteins be part of collectively into long-stranded fibrils that finally kind tangled clumps.
The crew noticed this exercise in a salt resolution, which they notice is way nearer to the pure surroundings in our brains than different laboratory imaging circumstances.
“Conventional methods, such as those based on staining techniques, could alter the morphology and adsorption site of the proteins so that they cannot be analyzed in their natural form,” Nirmalraj factors out.
Round 250 hours of remark beneath an atomic pressure microscope allowed the researchers to spy one thing uncommon.
A selected taste of amyloid beta proteins fold in such a approach that their edges are further reactive, as seen within the shiny areas of the above picture. This implies they extra readily accumulate further constructing blocks of themselves – extending their string-like fibrils by means of the mind faster than different sorts of amyloid beta do.
“A small population of fibrils that displayed higher surface catalytic activity was identified as superspreaders,” the crew writes of their paper.
These superspreaders, amyloid beta 42, kind solely as secondary constructions after an preliminary amyloid beta fibril has been created (see the diagram under).
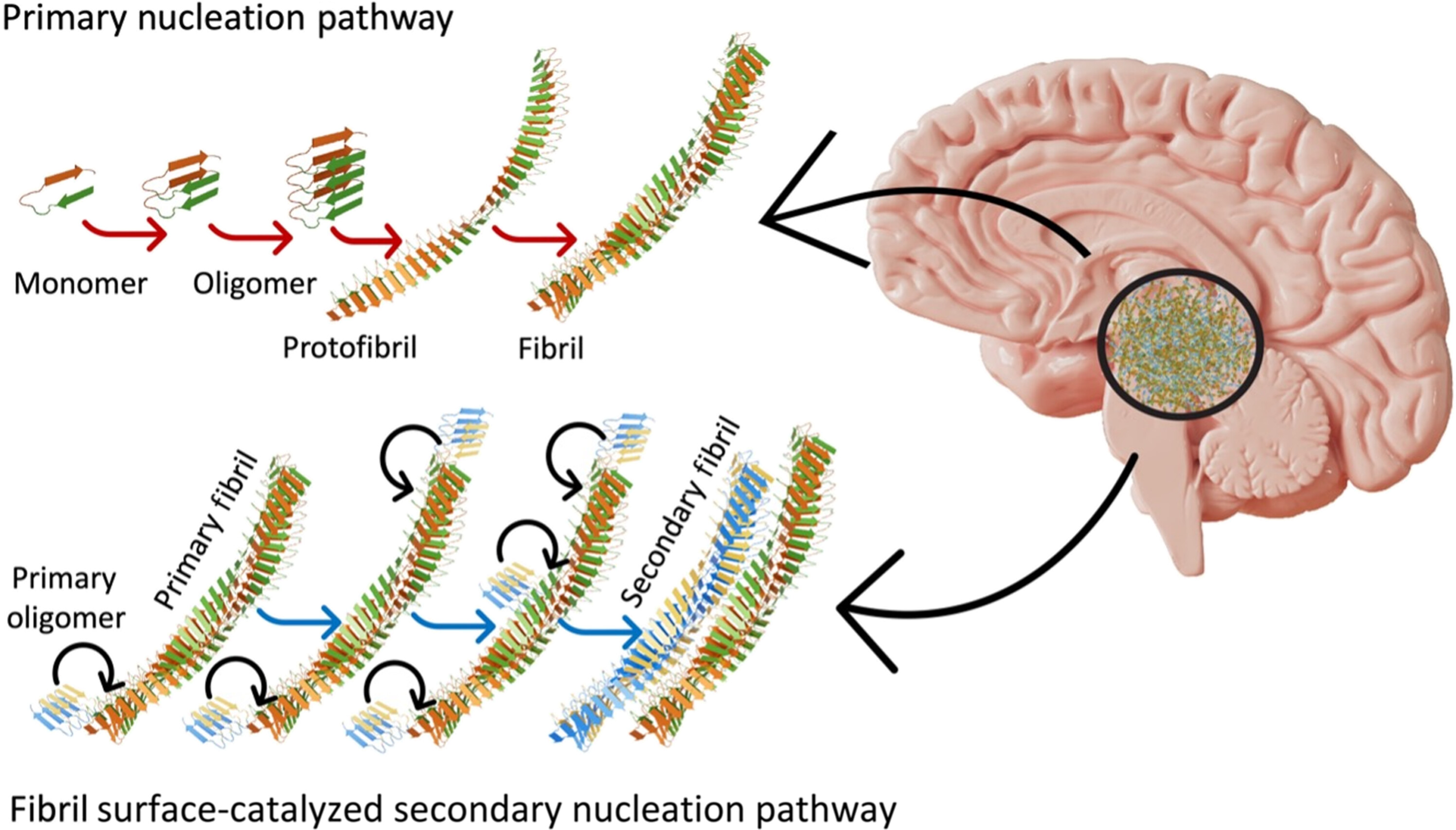
Nirmalraj and crew make clear the form and measurement of those protein clumps, however particulars of their construction are but to be resolved. These particulars embrace if and the way amyloid beta 42 differs chemically from different amyloid beta proteins, and what chemistry drives the expansion of those secondary constructions.
Earlier analysis has discovered that as amyloid beta proteins combination within the mind, individuals endure from more and more distressing signs comparable to reminiscence loss, impulsive conduct, nervousness, and confusion. That is nonetheless simply an affiliation and the direct mechanism for mind injury in dementia shouldn’t be but understood.
An enormous complexity of adjustments happen over a long time within the brains and our bodies of individuals creating neurodegeneration. So there are different theories that require continued exploration too, comparable to Alzheimer’s as an autoimmune illness.
This analysis was printed in Science Advances.

