October 2, 2024
4 min learn
Hurricanes Kill Individuals for Years after the Preliminary Catastrophe
The typical tropical cyclone within the U.S. finally causes about 7,000 to 11,000 extra deaths, new analysis finds
The Rocky Broad River flows into Lake Lure and overflows the city with particles from Chimney Rock, N.C., after heavy rains from Hurricane Helene on September 28, 2024. Roughly six ft of particles piled on the bridge from Lake Lure to Chimney Rock, blocking entry.
Melissa Sue Gerrits/Getty Photographs
Greater than 160 individuals have misplaced their lives to the ferocious winds and catastrophic flooding wrought by Hurricane Helene. However the true dying toll will take years—possible greater than a decade—to unfold.
A brand new examine revealed on Wednesday in Nature discovered that the common tropical cyclone within the U.S. finally causes about 7,000 to 11,000 extra deaths (these past what would sometimes be anticipated), in contrast with the common of 24 direct deaths reported in official statistics. The examine’s authors estimated that, between 1950 and 2015, tropical storms and hurricanes prompted between 3.6 million and 5.2 million extra deaths—greater than these attributable to visitors deaths or infectious ailments. And such storm-related deaths contain individuals from some teams greater than others, marking an “important and understudied contributor to health in the United States, particularly for young or Black populations,” the authors wrote.
“These are individuals who are dying years before they would have otherwise,” says examine co-author Rachel Younger, an environmental economist on the College of California, Berkeley.
On supporting science journalism
For those who’re having fun with this text, take into account supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world as we speak.
This examine is a part of a burgeoning development: assessing the complete well being penalties of the rising variety of disasters fueled by local weather change. Epidemiologists and different specialists have more and more been emphasizing that warmth wave deaths are considerably underestimated, and up to date analysis has discovered that wildfire smoke kills hundreds of individuals in California—many greater than the precise flames. “We thought that there was something similar with hurricanes,” Younger says.
So she and Stanford College economist Solomon Hsiang checked out hurricanes that hit the U.S. from 1930 to 2015, in addition to mortality information and used statistical strategies to check a state’s deaths earlier than a storm with those who occurred over the course of 20 years after from 1950 to 2015. “We thought we’d see maybe six months or a year of a delayed effect,” Younger says, however information confirmed extra deaths occurring for 15 years after a storm. “We were so stunned,” she says, that the researchers spent years testing and retesting to verify the impact was actual.
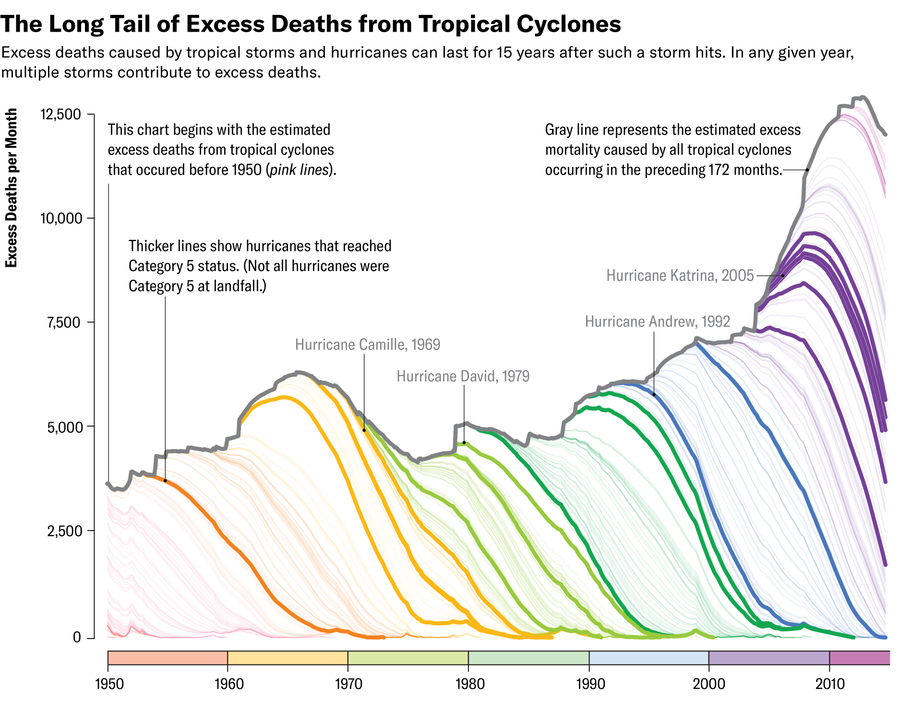
Zane Wolf; Supply: “Mortality Caused by Tropical Cyclones in the United States,” by Rachel Younger and Solomon Hsiang, in Nature. Printed on-line October 2, 2024
Considering past the information, the period of the impact is sensible as a result of “these are huge events,” Younger says. “Look at what’s going on with Helene.” Households might should spend months in broken or mold-riddled properties earlier than repairs are made. Individuals might have to make use of their financial savings for repairs, leaving much less cash for his or her well being look after years. Individuals could also be pressured to maneuver and stay farther away from essential social help networks. And these occasions exert a appreciable psychological well being burden. “It’s devastating to the individuals, and it’s devastating to the local and state governments, too,” Younger says, noting that different analysis exhibits these governments expertise finances declines for a few years after a hurricane. For these affected, she provides, “you’re in a version of the world where you have less money, you have less resources, you have more pollution exposure”—a foul mixture in the case of staying wholesome.
When breaking out the information by age teams, the examine discovered that individuals aged 65 and older had the most important variety of storm-related extra deaths. However when the upper common chance of dying on this age vary was factored in, this group’s storm dying threat was smaller than that of others. The most important threat was discovered to be for infants beneath the age of 1, with nearly all of those deaths occurring inside lower than two years after a storm. Younger says that this impact could possibly be influenced by individuals’s lack of ability to afford prenatal care in a storm’s wake, in addition to stress or different elements.
The chance of dying was additionally larger amongst Black individuals than it was amongst white individuals, although the white inhabitants that was uncovered to storms was a lot bigger than the uncovered Black inhabitants.
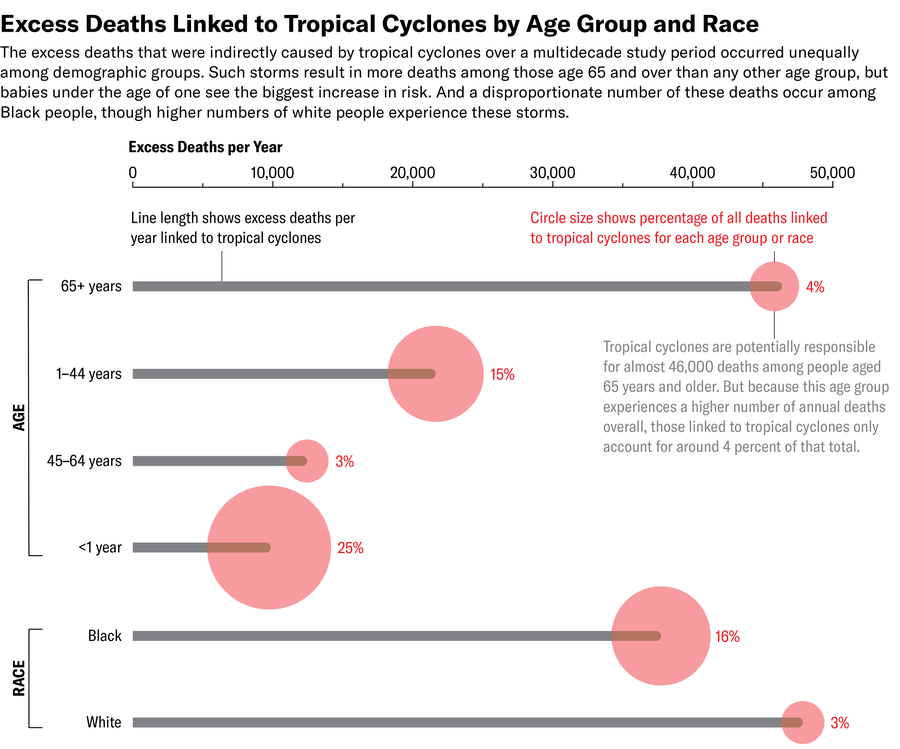
Zane Wolf; Supply:“Mortality Caused by Tropical Cyclones in the United States,” by Rachel Younger and Solomon Hsiang, in Nature. Printed on-line October 2, 2024 (information and reference determine)
The evaluation additional confirmed that “the mortality response isn’t going down over time,” Younger says, that means storms as we speak have the identical long-tail mortality impression as they did many years in the past. Younger and Hsiang don’t know precisely why that is the case and say it’ll take extra analysis to dig into the explanations.
That mortality discovering notably struck Eugenio Paglino, a postdoctoral researcher on the Helsinki Institute of Demography and Inhabitants Well being, who was not concerned with the brand new examine. He says that on first studying the paper’s summary, he thought the numbers of extra deaths the authors discovered “seemed pretty large,” however he felt they did an intensive job of checking the robustness of the outcomes. He want to see extra analysis study what would possibly really be inflicting these extra deaths and additional bolster the findings.
Younger and Hsiang additionally need to see this sort of follow-up analysis—and hope to do some themselves. It’s a vital step towards the final word purpose of informing policymakers of what’s wanted to safeguard communities within the face of the rising local weather catastrophe. As Helene exhibits, “local and state governments and first responders are doing heroic work to help people after disasters,” Younger says. “We don’t want their efforts to be in vain.”

