For a lot of the twentieth century, every successive decade added about three additional years to individuals’s common lifespan in developed nations. For an individual born on the flip of the twenty first century, these incremental positive aspects meant that they might, on common, stay 30 years longer than somebody born in 1900, permitting them to make it to their eightieth birthday.
This phenomenon, known as radical life extension, was gifted to humanity by advances in numerous medical applied sciences and public well being measures. Many scientists and lay individuals alike assumed that the pattern would proceed and that human lifespans would enhance on the identical clip indefinitely. Others, nevertheless, predicted that people would hit a pure ceiling, with common lifespans of the world’s longest-lived nations plateauing nicely earlier than 100.
New analysis on this hotly debated query now means that humanity has, in truth, reached an higher restrict of longevity. Regardless of ongoing medical advances designed to increase life, the findings point out that folks in probably the most long-lived nations have skilled a deceleration within the charge of enchancment of common life expectancy over the previous three many years.
On supporting science journalism
When you’re having fun with this text, take into account supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you’re serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world in the present day.
It’s because ageing—a collection of poorly understood organic processes whose results embody frailty, dementia, coronary heart illness and sensory impairments—has up to now eluded efforts to gradual it down, says S. Jay Olshansky, a professor of public well being on the College of Illinois at Chicago and lead writer of the brand new examine, which was printed in Nature Getting older. “Our bodies don’t operate well when you push them beyond their warranty period.”
“As people live longer, it’s like playing a game of Whac-a-Mole,” he provides. “Each mole represents a different disease, and the longer people live, the more moles come up and the faster they come up.”
Olshansky turned satisfied of the immutability of the ageing downside in 1990, when he printed a paper in Science that predicted that our positive aspects in life expectancy should decelerate, even when advances in medication speed up. He concluded then that it was “highly unlikely” that humanity would exceed a median life expectancy of 85 years.
The paper met with widespread pushback, he says, as a result of “there’s vested interest in this narrative of continued gains in life expectancy.”
Olshansky was satisfied he was proper, although. So he determined to “be a patient scientist,” he says, and retest his speculation as soon as the real-world knowledge got here in. It took 34 years, however the wait has now paid off with “a definitive yes” in assist of his unique findings, he provides.
Olshansky and his colleagues took an easy strategy: they examined noticed modifications in dying charges and life expectations from 1990 to 2019 on the earth’s eight longest-lived nations—Japan, South Korea, Australia, France, Italy, Switzerland, Sweden and Spain—plus the U.S. and Hong Kong. They discovered that enchancment in life expectancy decelerated in nearly all of those locations and that it truly declined within the U.S.
South Korea and Hong Kong have been exceptions. They underwent latest accelerated enhancements in survival, a phenomenon the researchers suspect has to do with the truth that each locations concentrated their giant will increase in life expectancy solely lately, previously 25 years, Olshansky says. Even so, in Hong Kong—whose inhabitants is the world’s longest-lived—the researchers discovered that simply 12.8 % of feminine youngsters and 4.4 % of male youngsters born in 2019 are anticipated to succeed in 100 years outdated.
The figures have been considerably decrease within the U.S., with solely 3.1 % of feminine youngsters and 1.3 % of male youngsters anticipated to stay to 100.
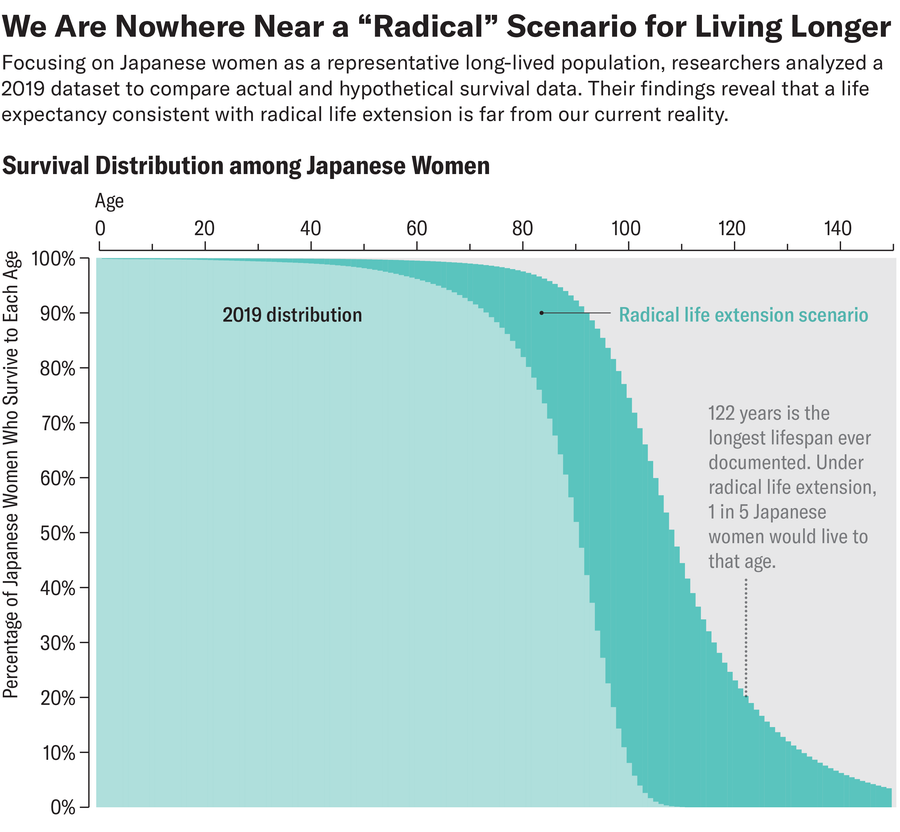
To place their findings into perspective, Olshansky and his colleagues additionally calculated what life expectancy would appear to be if humanity had truly stored tempo with radical life extension. If that had occurred, then 6 % of Japanese ladies, for instance, can be dwelling to the age of 150, and round one in 5 Japanese ladies can be dwelling previous 120. “We didn’t call those scenarios ‘ridiculous’ in our paper, but we were hoping people would come to that conclusion on their own,” Olshansky says.
The brand new paper’s strategy and conclusion “make perfect sense,” says Jan Vijg, a biologist and geneticist at Albert Einstein School of Drugs, who was not concerned within the analysis. “There is really no evidence that survival to 100 will become a reality any time soon.”
The brand new paper’s findings mirror some prior analysis, Vijg provides, together with a 2016 paper that he and his colleagues printed that reached the identical conclusion about lifespan limits. “After we published our paper, we got overwhelmed by an avalanche of responses, both scientifically and nonscientifically, that we were charlatans, that our data were flawed and that there was no evidence for a limit to life span,” Vijg says. “Needless to say, flaws in our data were never found.”
Regardless of the load of the brand new proof, Olshansky absolutely expects that he and his colleagues’ findings will probably be controversial.
He argues, although, that scientists ought to shift the main target away from the “untested hypothesis” of continued radical life extension and will as a substitute pivot to geroscience—a comparatively new discipline of analysis that’s centered on extending individuals’s “health span,” the variety of wholesome years that they must take pleasure in, however not their general lifespan. Until new applied sciences tackle ageing itself, additional radical life extension in already long-lived nations “remains implausible,” Olshansky and his colleagues wrote of their new paper.
Nalini Raghavachari, a program officer on the U.S. Nationwide Institute on Getting older, who was not concerned within the examine, agrees that analysis ought to concentrate on understanding and reaching wholesome ageing. Clues for a way to try this might come from a number of the world’s longest-lived populations, she says. “A deeper understanding of the protective influences and mechanisms underlying exceptional health span could lead to the development of novel therapeutic targets and interventions to promote healthy aging,” Raghavachari provides.

