Alone Tyrannosaurus rex sniffs the humid Cretaceous air, scenting a herd of Triceratops grazing past the tree line. Because the predator scans the floodplain, its imaginative and prescient out of the blue snaps into focus. A single Triceratops has damaged off from the herd and wandered inside putting distance. Standing immobile, the T. rex formulates a plan of assault, anticipating the exact angle at which it should intersect its goal earlier than the Triceratops can regain the security of the herd. The afternoon silence is shattered because the predator crashes although the low branches on the fringe of the forest in sizzling pursuit.
T. rex has hunted Triceratops in so many books, video games and flicks that the encounter has turn into a cliché. However did a scene like this one ever unfold in actual life? Would T. rex establish its prey by imaginative and prescient or by odor? Would the Triceratops be warned by a loudly cracking department or stay oblivious as a result of it was unable to find the supply of the sound? May T. rex plan its assault like a cat, or wouldn’t it lash out indiscriminately like a shark?
Ever since dinosaurs have been first described within the early 1800s, paleontologists have debated their intelligence, sensory capabilities and behavioral complexity. Early investigations relied on pure endocasts, that are casts shaped when sediment fills the empty area in a cranium. These casts replicate the form of the braincase’s contents in life. The traditional knowledge lengthy held that each one dinosaurs had tiny brains and subsequently unsophisticated behaviors. Maybe probably the most amusing instance of this view of dinosaur intelligence got here from Nineteenth-century paleontologist Othniel Charles Marsh, who hypothesized that the armored dinosaur Stegosaurus had a second mind close to its rump to complement the walnut-size mind in its cranium. This concept was primarily based on a vaguely braincase-shaped growth of the spinal canal close to the dinosaur’s pelvis. The mysterious growth is now thought to symbolize a glycogen physique—a construction that shops energy-rich glucose and happens in an identical place in some trendy birds.
On supporting science journalism
When you’re having fun with this text, think about supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales in regards to the discoveries and concepts shaping our world as we speak.
Current-day paleontologists stay unconvinced that Stegosaurus was able to a lot increased reasoning. However in recent times scientists’ appraisal of the cognitive capability of another dinosaurs has improved, significantly that of members of the theropod lineage that gave rise to birds. With the appearance of latest applied sciences, reminiscent of micro computed tomography (CT) scanning, we will now reconstruct the amount and floor topography of brains with out having to rely fully on uncommon pure endocasts, tremendously increasing the variety of species out there to check. Superior imaging can be educating us how dinosaurs might need used their brains. We now have the instruments wanted to reply the query of how long-vanished animals perceived the world round them and what actually occurred when predator met prey within the age of dinosaurs.
Wright here did T. rex fall on the intelligence spectrum between dim-witted Stegosaurus and tool-using ravens? In a high-profile paper printed final fall, neuroscientist Suzana Herculano-Houzel of Vanderbilt College steered {that a} T. rex was about as sensible as a baboon—a startling conclusion as a result of primates, with their massive brains, are a number of the cleverest animals round. Having spent lengthy hours pondering the way in which mind quantity scales with physique measurement and what this relation means for mind perform in extinct dinosaurs and birds, we have been intrigued to see the headlines about this research. Superficially, the mind of the tyrant lizard king seems pretty puny in contrast with its physique measurement. Weighing in at lower than a pound, the mind of this six-ton dinosaur is diminutive subsequent to the 11-pound mind of the African elephant, which, regardless of being the most important dwelling terrestrial mammal has a smaller physique than T. rex.
Herculano-Houzel argued that the relation between mind measurement and physique measurement is unimportant in terms of intelligence. What issues, she mentioned, is the uncooked variety of neurons within the telencephalon, a area within the entrance of the mind that features not solely the olfactory bulbs that course of odor but in addition the cerebrum, the place increased cognitive capabilities reminiscent of decision-making happen. Scientists beforehand had solely an imprecise understanding of what number of neurons have been current in vertebrate brains as a result of in numerous species they are often roughly densely packed in numerous components of the mind.
A T. rex with the intelligence of a primate can be terrifying. We expect some caveats are so as, nonetheless.
Herculano-Houzel and Roberto Lent of Federal College of Rio de Janeiro invented a way for counting neurons referred to as the isotropic fractionator technique. It makes use of particular chemical substances to dissolve a mind, primarily making mind soup. A fluorescent dye stains the nuclei of neurons in order that they glow and are simply seen. Researchers can exactly rely the glowing nuclei in a small, homogeneous pattern of the soup after which extrapolate the whole variety of neurons within the dwelling mind. Utilizing this technique, Herculano-Houzel and her colleagues calculated that human brains have roughly 100 billion neurons, confirming earlier estimates.
The isotropic fractionator technique is intelligent, however scientists won’t ever have an precise T. rex mind to dissolve. As an alternative Herculano-Houzel relied on the scaling relation between telencephalon measurement and neuron numbers for dwelling warm- and cold-blooded species, plugging extinct dinosaurs into one in every of two equations primarily based on their inferred metabolism. This scaling relation varies tremendously amongst vertebrates. Chilly-blooded, or ectothermic, species are likely to have much less tightly packed neurons than warm-blooded, or endothermic, species.
For instance, isotropic fractionator knowledge reveal {that a} 159-pound Nile crocodile has about 81.5 million neurons, whereas a 73-pound emu has roughly 1.3 billion neurons—nearly 16 instances as many because the crocodile regardless of being solely half its measurement. Herculano-Houzel contended that the majority theropod dinosaurs have been in all probability endothermic and thus close to the chicken finish of the neuron-density continuum. Beneath this assumption, a T. rex telencephalon weighing roughly 12 ounces would include round three billion neurons, on par with these of many primates.
A T. rex with the intelligence of a primate can be terrifying. We expect some caveats are so as, nonetheless. In addition to the affordable supposition that theropods have been endothermic, the estimate of three billion neurons depends on just a few different assumptions. One is that all the braincase was occupied by the mind, which is clearly not true primarily based on the morphology of T. rex endocasts. Fossil proof signifies that in lots of dinosaurs, buildings reminiscent of sinuses and blood vessels took up substantial components of the braincase. Precise mind quantity would have been smaller than uncooked endocranial quantity. In actual fact, research primarily based on trendy crocodilians counsel that the mind of T. rex might need occupied as little as 30 % of the general endocranial quantity.
It’s additionally essential to notice that totally different mind areas have totally different capabilities. Some are dedicated to duties as primary because the regulation of respiratory, whereas others help capabilities as complicated as language. Two species with the identical telencephalon measurement could have vastly totally different cognitive capacities if the cerebrum dominates the mind measurement of 1 and enlarged olfactory bulbs dominate the mind measurement of the opposite. For dwelling species, it’s potential to find out the boundaries between totally different mind areas with methods reminiscent of cell staining or magnetic resonance imaging.
T. rex actually would have been capable of sniff the wind and establish each dwelling prey and carcasses to scavenge lengthy earlier than laying eyes on them.
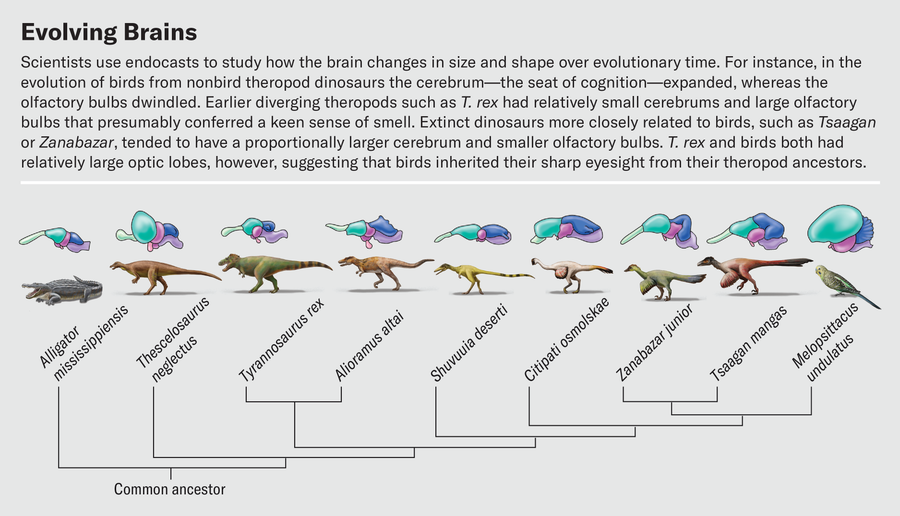
Defining these boundaries is way more durable for dinosaurs as a result of all we’ve got to work from is the floor topology. One among us (Balanoff) has spent a big a part of her profession mapping out bony landmarks that enable for higher estimates of the volumes of main mind areas from endocasts. This work has proven that growth of the cerebrum arose in additional specialised theropods reminiscent of oviraptorosaurs and dromaeosaurs—lineages that branched off a lot later than tyrannosaurids. In distinction, earlier-diverging theropods reminiscent of T. rex had comparatively small cerebrums, with a big portion of the general telencephalon given over to the olfactory bulbs.
As soon as we account for the amount of nonneural tissues housed within the endocast, it’s unlikely that T. rex had three billion neurons of any form in its telencephalon. We agree that T. rex was a proficient predator, however we argue that it was in all probability not able to the superior planning or coordinated social looking seen in primates.
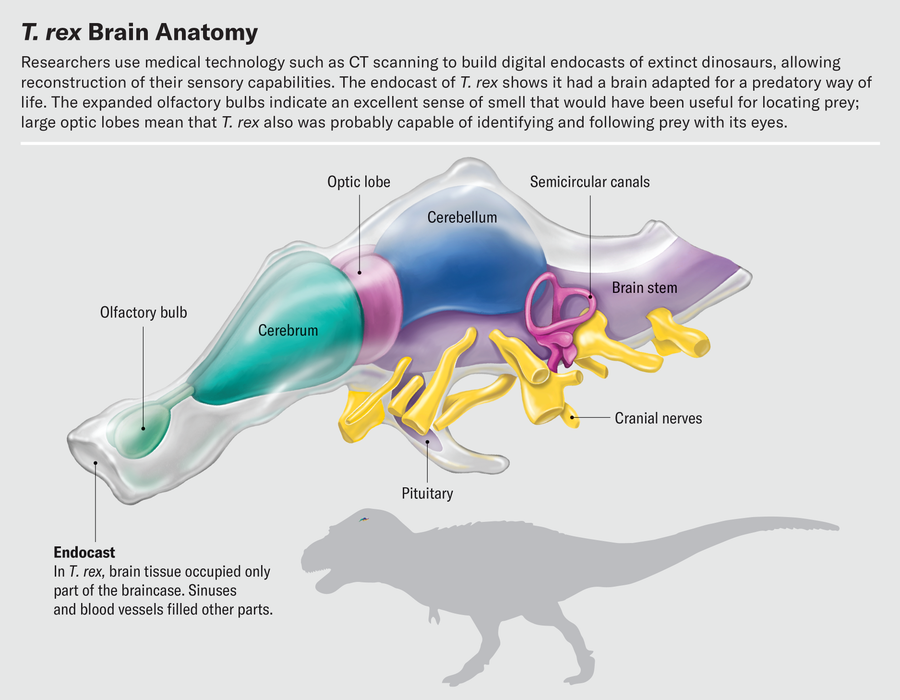
One of the most effective issues about working with fossil endocasts constructed from CT scans is that we will research inside options with out damaging the fossils themselves. Just about chopping up fossil endocasts is a pleasant strategy to spend a day. Exploring the mind slice by slice, a skilled paleontologist can use bony landmarks to decipher the boundaries of key mind areas and isolate these areas digitally. As we section the mind from entrance to again, the olfactory bulb is the primary construction we encounter. Olfactory bulb form varies dramatically in dinosaurs and their family. Alligator olfactory bulbs are in regards to the measurement of small grapes and are positioned on the finish of lengthy stalks resulting in the remainder of the mind. The olfactory bulbs of most birds are a lot smaller; in reality, in lots of species they’re barely distinguishable from the remainder of the cerebrum.
Because the identify implies, the olfactory bulb facilitates odor—a way that depends on tiny molecules referred to as odorants. Inhaled odorants bind to receptors within the nasal tissue, which talk through neurons to the olfactory bulbs. Amazingly, every receptor makes a single odorant-receptor protein, which is tuned to particular kinds of odorants. Every of those proteins is coded by a special olfactory receptor gene. Genomic sequencing has revealed that birds have anyplace from 182 to 688 purposeful olfactory receptor genes.
In a latest research, Graham Hughes and John Finarelli of College School Dublin investigated dinosaurs’ sense of odor. The variety of olfactory receptor genes in dinosaurs can’t be measured straight, however as a result of bulb measurement correlates to the variety of receptors, bulb dimensions can function a proxy for a way properly the animals might detect odors. Hughes and Finarelli discovered that, normally, dinosaurs had proportionally bigger olfactory bulbs than birds. Amongst theropods, the omnivorous ornithomimosaurs had the smallest olfactory bulbs, and carnivorous species had the most important. Tyrannosaurus topped the charts with olfactory bulb dimensions according to the presence of greater than 600 olfactory receptor genes. This quantity is on par with home cats and better than in nearly all trendy birds. Our hypothetical Triceratops-stalking T. rex actually would have been capable of sniff the wind and establish each dwelling prey and carcasses to scavenge lengthy earlier than laying eyes on them.
Mesa Schumacher; Sources: “New Insights into the Brain, Braincase, and Ear Region of Tyrannosaurs (Dinosauria, Theropoda), with Implications for Sensory Organization and Behavior,” by Lawrence Witmer and Ryan Ridgely, in The Anatomical Document, Vol. 292; 2009, and “Gross Anatomical Brain Region Approximation (GABRA): Assessing Brain Size, Structure, and Evolution in Extinct Archosaurs,” by Ashley Morhardt, Doctoral dissertation, Ohio College, 2016 (endocast references)
Different work on CT-based endocasts hints at how sharp T. rex’s eyes have been. By nearly slicing up endocasts and isolating the optic lobes, we’ve got discovered that the relative sizes of those buildings have been related in extinct theropods and dwelling birds. Birds subsequently will need to have inherited their visible acuity from their nonbird ancestors. Birds are recognized to be extremely visible animals—an eagle can spot a rabbit from half a mile away, and a tern in flight can observe a fish half an inch lengthy beneath the floor of water and decide it off from above. This reliance on sight is mirrored within the construction of the chicken mind. The optic lobes, which course of visible info and reside simply behind the cerebrum, are a number of the mind’s most outstanding options. It’s typically true that the bigger a area is relative to the remainder of the mind, the extra essential that area is to the animal. This definitely holds for the optic lobes.
We will infer some visible capacities of extinct dinosaurs from their evolutionary relationships. For instance, each birds and crocodilians—the closest dwelling family of the extinct dinosaurs—have the kinds of retinal receptors wanted to see in colour. So dinosaurs more than likely had colour imaginative and prescient, too. Imaginative and prescient is a sophisticated sense, nonetheless. Precisely reconstructing simply how properly extinct dinosaurs might see requires us to transcend most of these inferences.
One issue that makes predatory birds so adept at capturing prey is stereoscopic imaginative and prescient—an enhanced skill to understand depth. The sensory adaptation that underlies this subtle functionality is astonishingly easy. It merely has to do with the place of the eyeballs. Animals with eyes positioned on the aspect of the pinnacle, reminiscent of geckos, lack overlapping visible fields, so that they don’t see properly in three dimensions. Animals with eyes positioned on the entrance of the pinnacle have visible fields that overlap in entrance of the nostril. Inside this overlapping area, every eye perceives the identical info from a barely totally different perspective, producing what is named binocular imaginative and prescient.
Attempt fixing your gaze on an object a few foot or so in entrance of you, then closing one eye after which the opposite. The article will appear to maneuver since you’re seeing the identical picture in entrance of your nostril however from totally different angles. The mind integrates these barely totally different pictures to supply visible depth. Animals with laterally positioned eyes choose depth by one thing with one eye, transferring their head after which it with the opposite eye—not an particularly stealthy method. For a predator, binocular imaginative and prescient is especially helpful as a result of it permits the animal to establish and nil in on prey with out doubtlessly disclosing its location by transferring its head.
To find out whether or not extinct animals had stereoscopic imaginative and prescient, we should think about the place of their orbits, that are the areas within the cranium that home the eyeballs. Kent Stevens of the College of Oregon took a artistic method to this query by sculpting the heads of a number of theropod dinosaurs primarily based on their skeletal construction. From there he was capable of map their visual field, together with any obstructions reminiscent of horns or an particularly massive snout. He discovered that T. rex had forward-facing eyes and a slim snout that wouldn’t hinder its view, giving it a visible acuity just like that of hawks. In contrast to the fictional T. rex in Jurassic Park, an actual T. rex wouldn’t have wanted its prey to maneuver to choose it out from the background. Deinonychosaurs reminiscent of Troodon and Velociraptor have been in all probability much more adept at figuring out their prey. With their heads barely tilted ahead, they’d wider fields of imaginative and prescient and enhanced depth notion doubtlessly rivaling that of owls.
We will infer greater than the power to understand depth from the orbits of extinct animals. The scale of those openings and their related bones present hints in regards to the measurement of the eyeballs they housed. Bigger orbits usually point out bigger eyeballs. Eyeballs which can be massive relative to the dimensions of the pinnacle are frequent amongst nocturnal animals as a result of they’ll accommodate bigger numbers of light-sensitive photoreceptors within the retina. Furthermore, the eyeballs of many animals, together with fish, some extinct mammals, and reptiles (nonbird dinosaurs and birds amongst them), have bony or cartilaginous rings embedded inside the fibrous outer layer of the eyeball often called the sclera. As a result of bone is inflexible, these scleral rings constrain the actions of the eyeball, together with how far the pupil can open. This impacts how a lot gentle reaches the photoreceptors within the retina. Bigger scleral rings enable the pupils to open wider, thereby letting extra gentle into the attention.
A number of years in the past Balanoff was a part of a workforce led by Jonah Choiniere of the College of the Witwatersrand in South Africa that studied the dimensions of those rings within the orbits of nonbird dinosaurs to find out whether or not they most well-liked to maneuver about in the course of the daytime or at night time. As a result of the scleral rings will not be hooked up to any a part of the cranium, they’re simply disassociated from the remainder of the skeleton and infrequently preserved in fossils. Within the uncommon specimens that retain them, they aren’t all the time present in place. For this research, the researchers used CT pictures of extinct dinosaurs with preserved scleral rings to digitally isolate these bones and reconstruct them inside the orbit. They concluded that the proportions of their orbits and scleral rings counsel many extinct dinosaurs have been energetic primarily in the course of the daytime.
However one house-cat-size alvarezsaurid theropod, Shuvuuia deserti, offered a special consequence. The workforce examined a Shuvuuia cranium found in Late Cretaceous desert dune deposits from Mongolia and have been startled to seek out diversifications convergent with one of many best-known dwelling nocturnal animals, the barn owl. Barn owls have massive orbits with ample scleral rings, which permit their pupils to open very large. This association lets an infinite quantity of sunshine flood into the attention, offering an image within the darkest of circumstances. The presence of those similar options in alvarezsaurids means that they, too, have been energetic nighttime predators.
Nobody has formally analyzed the orbit morphology of T. rex for insights into when the dinosaur was most energetic. We do know, nonetheless, that T. rex had a big orbit formed nearly like a keyhole. If the attention had stuffed all the orbit, then we’d have the ability to infer that T. rex was nocturnal, however scleral rings from carefully associated species counsel that its eyeball stuffed solely a small portion of the orbit—and thus may not have been capable of collect sufficient gentle to be of a lot use at night time. In actual fact, digital analyses of cranium stresses led by Stephan Lautenschlager of the College of Birmingham in England point out that the massive orbit of T. rex helped to disperse the massive stresses generated by its forceful chew moderately than accommodating a giant eye.
Near the rear of the vertebrate cranium is an attention-grabbing and sophisticated construction: the interior ear. Although not technically a part of the mind, it is a crucial sensory organ that sends a variety of info to the mind. Two particular senses, stability and listening to, are managed by separate components of the interior ear’s so-called labyrinth. The labyrinth contains the semicircular canals, looplike buildings that detect rotational motion of the pinnacle; the vestibule, a bloblike construction that senses back-and-forth and side-to-side actions; and the cochlea, which senses sound vibrations. The interior ear is stuffed with fluid and makes use of deflection of hair cells inside that fluid to detect these various kinds of info.
In 2021 Michael Hanson, now on the Smithsonian Establishment, and his colleagues carried out a classy evaluation of the form of the semicircular canals and vestibule to deduce the dominant mode of locomotion in nonbird dinosaurs. They made digital endocasts of the interior ear area to estimate what the labyrinth would have regarded like throughout life. Their knowledge point out that the majority dinosaurs have been restricted to strolling and working alongside the bottom. However within the lineage that led to birds, the construction of the ear modified. Amongst different shifts, the semicircular canals grew longer. This elongation allowed dinosaurs to make and interpret extra complicated actions of the pinnacle. T. rex didn’t have lengthy semicircular canals, suggesting that it was able to solely strolling or working. However some troodontid dinosaurs extra carefully associated to Velociraptor had an ear that might sense the complicated actions related to flight. These dinosaurs have been in all probability able to gliding or a rudimentary type of flight, transferring by means of the air earlier than trendy birds took wing.
We will look to the cochlea for clues to dinosaurs’ listening to. The size of the cochlea is correlated with listening to sensitivity. An extended cochlear duct permits for an elongation of the basilar papilla, the construction that holds the hair cells that decide up sound vibrations. Lizards and turtles are likely to have quick, stubby cochleas greatest suited to detecting low-pitch sounds. Crocodilians and birds, in distinction, have for much longer, slenderer cochleas that excel at detecting higher-pitched sounds.
Many birds sing melodious songs to draw mates and defend their territory, so it might sound becoming that they’ve elevated sensitivity to high-pitched vocalizations. But the elongation of the cochlea originated not in birds however within the frequent ancestor of birds and crocodilians. The bizarre factor is, croc vocalizations are restricted to low-pitched, closed-mouth grunts—not the sorts of sounds that an elongated cochlea excels at detecting. Precisely why crocodilians have such a sophisticated cochlea form in contrast with different reptiles was a thriller.
Hanson and his collaborators proposed a intelligent clarification. They hypothesized that the elongation of the cochlea that differentiates crocodilians, extinct dinosaurs and birds from earlier-diverging reptiles has to do with the evolution of parental care. In contrast to most reptiles, crocodilians care for his or her younger. And in contrast to most younger reptiles, crocodilian infants chirp to get their dad and mom’ consideration. Maybe the ancestors of birds and crocs wanted to have the ability to detect high-pitched sounds to listen to their younger moderately than mates or rivals.
Like trendy predators, T. rex had a proportionally massive mind in contrast with its plant-eating quarry.
This speculation has thrilling implications for the evolution of birdsong. On this state of affairs, juvenile dinosaurs might have chirped for consideration, however adults have been restricted to producing easy low-pitched calls. Over the course of the dinosaur-bird transition, some lineages retained the capability for high-pitched vocalizations into maturity. Cochlear elongation, initially favored by pure choice for its function in enhancing parental care, then served as a preadaptation that allowed music to come up in later birds.
However evolution doesn’t transfer in a single route. Sifting by means of the dinosaur knowledge, Hanson and his colleagues discovered an unusually quick cochlea in Alioramus, a cousin of Tyrannosaurus. This discovery steered that the massive theropod had misplaced sensitivity to higher-pitched sounds. The workforce speculated that Alioramus might need left its younger unattended, eradicating the choice stress for listening to their vocalizations.
The form of the cochlea has additionally helped us perceive the ecology of these oddball nocturnal alvarezsaurids. Balanoff and her colleagues discovered that the cochlea of Shuvuuia was so lengthy that it curled underneath the bottom of the cranium. Nocturnal birds reminiscent of owls are recognized to have an identical association. The hyperelongated cochlear duct of Shuvuuia signifies that its listening to was attuned to very high-frequency sounds reminiscent of these produced by bugs. The workforce concluded that this small dinosaur prowled the desert dunes of Central Asia within the darkness, attempting to find these small prey.
People have a tendency to think about paleontology as a field-primarily based self-discipline, specializing in the romantic attract of summers spent in distant desert locales with pickax in hand, accumulating fossils of long-extinct animals new to science. However lately paleontologists are simply as more likely to make their most vital discoveries within the laboratory utilizing cutting-edge applied sciences from biomedicine and neuroscience. It’s the mixture of those disparate approaches that permits us to reconstruct what actually might need gone down when T. rex encountered Triceratops.
Our personal analysis tells us that like trendy predators, T. rex had a proportionally massive mind in contrast with its plant-eating quarry. A considerable a part of its mind was dedicated to olfaction, so Tyrannosaurus in all probability did sniff the air to find its subsequent meal, whether or not it was the dwelling Triceratops grazing alongside the tree line or one which was already useless and rotting within the solar. As soon as the T. rex remoted a scent, it might then scan the horizon with its stereoscopic imaginative and prescient for any signal of potential prey. Its eyes would have been capable of repair on that Triceratops obliviously feeding on a cluster of vegetation removed from the security of its herd.
Because the T. rex crashed by means of the timber, it might need startled a small troodontid dinosaur nesting within the branches close by. With the improved locomotor abilities afforded by its expanded interior ear labyrinth, the troodontid might need glided off its nest, distracting the predator from its chirping younger. Unsettled by this commotion, the Triceratops might need stopped its peaceable grazing and returned to the security of its herd. It’s nonetheless a clichéd story however one that’s rather more scientifically knowledgeable.

