The arithmetic Albert Einstein devised to explain the gravitational workings of the bodily Universe within the early twentieth century remains to be holding sturdy.
In one of many largest checks of normal relativity up to now, an enormous crew of astronomers has mapped the distribution of almost 6 million galaxies throughout 11 billion years of the Universe’s historical past.
The best way gravity clumps these galaxies collectively alongside strands of the cosmic net in opposition to the outward pull of the enlargement of the Universe, and the best way that net evolves over time, is strictly in keeping with predictions made by Einstein’s well-known concept.
It’s, maybe, the most important check of normal relativity up to now, spanning a lot of the 13.8-billion-year historical past of the Universe – that means that the speculation holds up on the largest scales in addition to the smallest.
The findings have been submitted for publication, and can be found in three new preprints uploaded to arXiv forward of peer assessment.
“General relativity has been very well tested at the scale of solar systems, but we also needed to test that our assumption works at much larger scales,” says cosmologist Pauline Zarrouk of the French Nationwide Middle for Scientific Analysis.
“Studying the rate at which galaxies formed lets us directly test our theories and, so far, we’re lining up with what general relativity predicts at cosmological scales.”
Gravity is prime to the best way the Universe works. We do not know what it’s or why it’s, simply that objects with mass have a tendency to draw different objects with mass; that the energy of the attraction is straight proportional to the mass; and that it alters the geometry of space-time round a mass.
It additionally behaves like a glue that attracts the Universe collectively. Massive filaments of gravitational fields generated by darkish matter span your entire Universe in a kind of net; and a lot of the matter within the Universe is distributed alongside the strands and nodes of this cosmic net.
It is predictable and measurable and, thus far, extraordinarily nicely constrained and outlined by the speculation of normal relativity. However discovering flaws within the concept may reveal options to some remarkably thorny issues, such because the irreconcilable variations between quantum mechanics and classical physics. So scientists preserve poking it to see if the Universe’s contents look simply how normal relativity says it should, on all scales.
This brings us to the Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory-led Darkish Vitality Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI), an enormous worldwide collaboration that’s at present working to map the observable Universe to unravel its largest secrets and techniques. It has been operational since 2019; the brand new outcomes are primarily based on an in depth and prolonged evaluation of simply the primary 12 months of information obtained by the instrument.
The DESI Collaboration used that information to conduct a painstaking survey of 5.7 million galaxies and quasars throughout the historical past of the Universe, mapping their progress, evolution, and distribution alongside the cosmic net from the early Universe 11 billion years in the past.
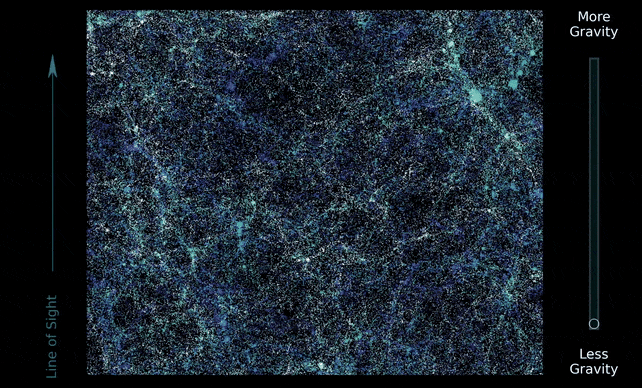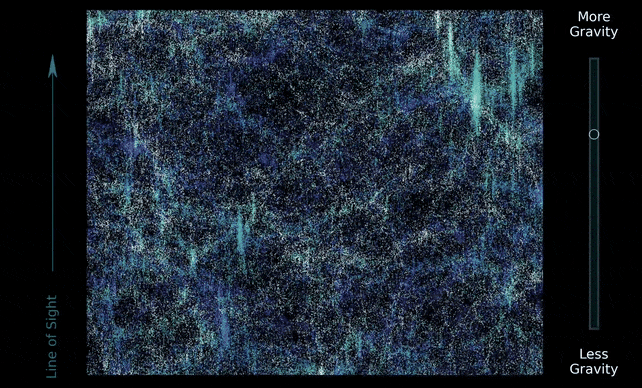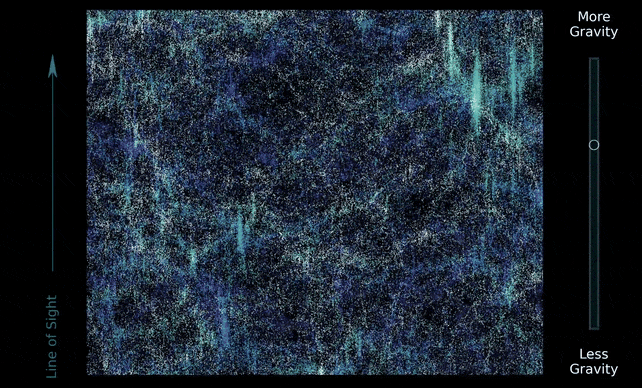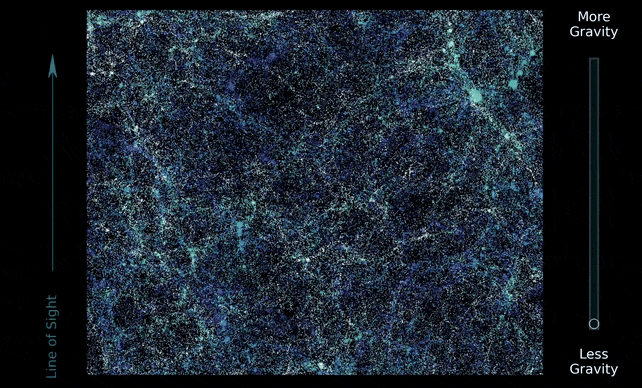
They used the speculation of normal relativity to foretell the cosmic net’s progress and distribution, and located that the Universe we stay in has behaved the best way relativity says it ought to, on an epic cosmic scale. Add extra gravity, or take some away, and the Universe would now not look the identical.
The outcome follows a paper earlier this 12 months that measured the enlargement fee of the Universe primarily based on cosmic relics of acoustic waves that froze when the atomic fog that crammed the early Universe cleared. The DESI Collaboration hopes that ongoing efforts will proceed to make clear the evolution of the Universe and, in flip, the mysterious forces that drive it.
“This is the first time that DESI has looked at the growth of cosmic structure,” says physicist Dragan Huterer of the College of Michigan. “We’re showing a tremendous new ability to probe modified gravity and improve constraints on models of dark energy. And it’s only the tip of the iceberg.”

The outcomes additionally positioned constraints on the higher restrict for the mass of the neutrino, a particle so ‘ghostly’ that we have been unable to weigh it exactly.
The survey remains to be ongoing, as is the Collaboration’s work. The researchers are at present analyzing the information from the primary three years of DESI’s operation. By the point the instrument completes its work, it’s going to have collected information on greater than 40 million galaxies and quasars.
Among the many keenest hopes is that it’s going to assist reveal the character of darkish matter, the mysterious invisible one thing answerable for producing further gravity within the Universe; and darkish power, the mysterious invisible one thing answerable for driving the variably accelerating enlargement of the Universe.
“Dark matter makes up about a quarter of the Universe, and dark energy makes up another 70 percent, and we don’t really know what either one is,” says physicist Mark Maus of Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory and the College of California Berkeley.
“The idea that we can take pictures of the Universe and tackle these big, fundamental questions is mind-blowing.”
The crew’s papers at the moment are obtainable on preprint server arXiv.

