Superbugs which might be immune to current antibiotics are a rising well being downside all over the world. Globally, almost 5 million folks die from antimicrobial resistant infections every year.
The annual toll of antimicrobial resistant infections is anticipated to rise by 70%, with an estimated 40 million deaths between now and 2050.
To handle this, researchers should uncover new antibiotics and brokers that enhance the efficacy of current antibiotics.
Hope could come from a shocking supply: oysters.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
In new analysis printed at the moment in PLOS ONE, we present that antimicrobial proteins remoted from oyster hemolymph (the equal of blood) can kill sure micro organism accountable for a spread of infections. The proteins may also enhance the efficacy of standard antibiotics towards problematic micro organism species.
Strong, resistant micro organism trigger widespread infections
Pneumonia is an acute an infection of the lungs, generally brought on by Streptococcus pneumoniae. It’s the main reason for loss of life amongst youngsters below 5 years of age, and a standard reason for hospitalisation and loss of life in older folks.
Higher respiratory tract infections, comparable to tonsillitis, are additionally widespread. In truth, they’re the most frequent motive youngsters are prescribed antibiotics.
Persistent pores and skin and throat infections brought on by Streptococcus pyogenes can result in the event of acute rheumatic fever and rheumatic coronary heart illness.
The excessive prevalence of those bacterial infections and overuse of antibiotics have contributed to the evolution of drug-resistant micro organism. This makes these infections tough to deal with.
The formation of biofilms compounds the issue.
Biofilms are populations of thousands and thousands of bacterial cells embedded in a self-secreted substance that sticks to surfaces. They defend micro organism from the host’s immune system – and from antibiotics. Nearly all bacterial infections contain biofilms.
Due to this, new antibiotic remedies that may inhibit, disrupt or penetrate biofilms are very worthwhile.
Oysters as a supply of recent antimicrobial brokers
Over 90% of antibiotics we at present use are derived from nature. The identical is true for over 65% of antibiotics below latest growth.
Within the seek for new antimicrobial medicine, researchers will normally begin by organisms that produce antimicrobial chemical substances for self defence.
Oysters are uncovered to excessive concentrations of various microorganisms of their pure marine surroundings. Due to this, they’ve developed sturdy immune defences. For instance, they rely closely on antimicrobial proteins and strings of molecules often called peptides of their hemolymph (blood) to guard them from an infection.
Analysis over the previous few a long time has discovered that oyster hemolymph accommodates antiviral and antibacterial proteins and peptides. These are lively towards a spread of human and marine pathogens.
Oysters, together with different molluscs, vegetation and animals, have an extended historical past of use as conventional medicines to deal with infectious illnesses.
In conventional Chinese language medication, numerous preparations from oysters are really useful for treating signs of respiratory an infection and inflammatory circumstances. Oysters have additionally performed a big position within the well being of Indigenous folks in Australia for millennia. This gives helpful clues for drug discovery.
Our newest analysis confirms that antimicrobial proteins within the hemolymph of Sydney rock oysters (Saccostrea glomerata) are notably efficient at killing Streptococcus spp. micro organism.
The proteins had been additionally efficient at inhibiting Streptococcus spp. biofilm formation and will penetrate biofilms that had already fashioned.
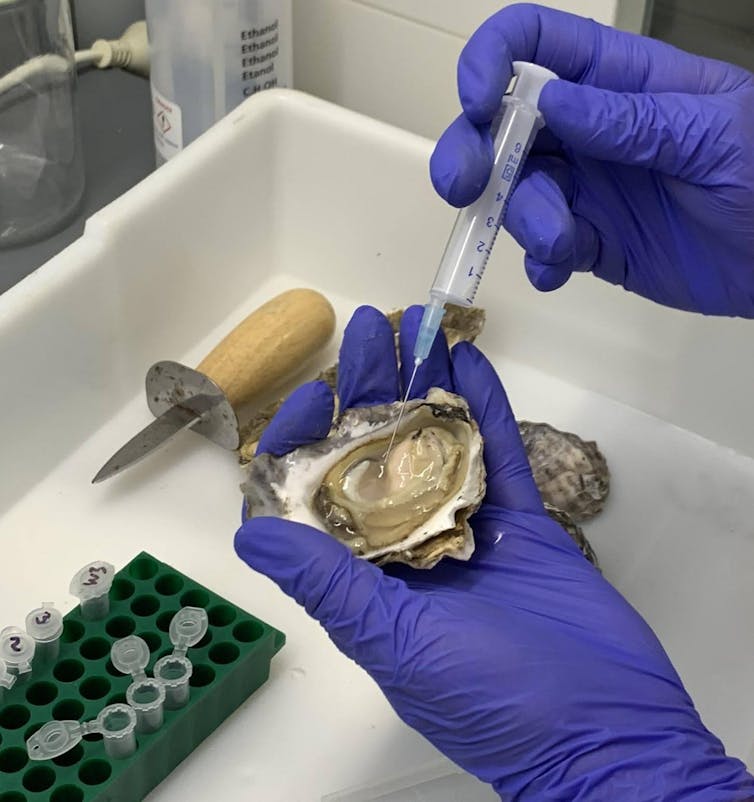
Boosting the medicine we now have
To enhance how nicely at present accessible medicine work, they’re more and more mixed with antimicrobial peptides and proteins.
These peptides and proteins can disrupt bacterial cell membranes, serving to standard antibiotics attain their targets extra simply. Many of those proteins and peptides may also enhance the host’s immune system, making therapy much more efficient.
We examined Sydney rock oyster hemolymph proteins for exercise towards a spread of bacterial pathogens together with totally different commercially accessible antibiotics. At very low concentrations, the proteins improved the effectiveness of antibiotics between two- and 32-fold.
The outcomes had been notably promising for Streptococcus spp., Staphylococcus aureus (also called “golden staph”, a major reason for drug-resistant pores and skin and bloodstream infections) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (a significant downside for immune-compromised sufferers with cystic fibrosis). There have been additionally no poisonous results on wholesome human cells.
What subsequent?
General, oyster hemolymph proteins maintain promise for future growth as an antimicrobial remedy. They will kill pathogens embedded in biofilms, work in synergy with standard antibiotics, and are non-toxic.
Nevertheless, extra work is required, together with testing in animals and medical human trials.
Sustainable provide of the proteins for analysis and medical use is a crucial consideration, however that is helped by the actual fact Sydney rock oysters are commercially accessible.
The outcomes of this work current a possibility for pharmaceutical and aquaculture industries to collaborate with researchers on new, more practical antibiotics growth.![]()
Kate Summer season, Postdoctoral analysis fellow, Southern Cross College and Kirsten Benkendorff, Professor, Nationwide Marine Science Centre, Southern Cross College
This text is republished from The Dialog below a Inventive Commons license. Learn the unique article.

