Fifteen years in the past cosmologists have been flying excessive. The easy however wildly profitable “standard model of cosmology” might, with just some substances, account for lots of what we see within the universe. It appeared to elucidate the distribution of galaxies in area as we speak, the accelerated enlargement of the universe and the fluctuations within the brightness of the relic glow from the massive bang—referred to as the cosmic microwave background (CMB)—primarily based on a handful of numbers fed into the mannequin. Certain, it contained some unexplained unique options, equivalent to darkish matter and darkish vitality, however in any other case all the pieces held collectively. Cosmologists have been (comparatively) blissful.
Over the previous decade, although, a pesky inconsistency has arisen, one which defies straightforward clarification and should portend vital breaks from the usual mannequin. The issue lies with the query of how briskly area is rising. When astronomers measure this enlargement price, often known as the Hubble fixed, by observing supernovae within the close by universe, their outcome disagrees with the speed given by the usual mannequin.
This “Hubble tension” was first famous greater than 10 years in the past, nevertheless it was not clear then whether or not the discrepancy was actual or the results of measurement error. With time, nonetheless, the inconsistency has turn into extra firmly entrenched, and it now represents a serious thorn within the aspect of an in any other case succesful mannequin. The newest knowledge, from the James Webb House Telescope (JWST), have made the issue worse.
On supporting science journalism
In case you’re having fun with this text, take into account supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales in regards to the discoveries and concepts shaping our world as we speak.
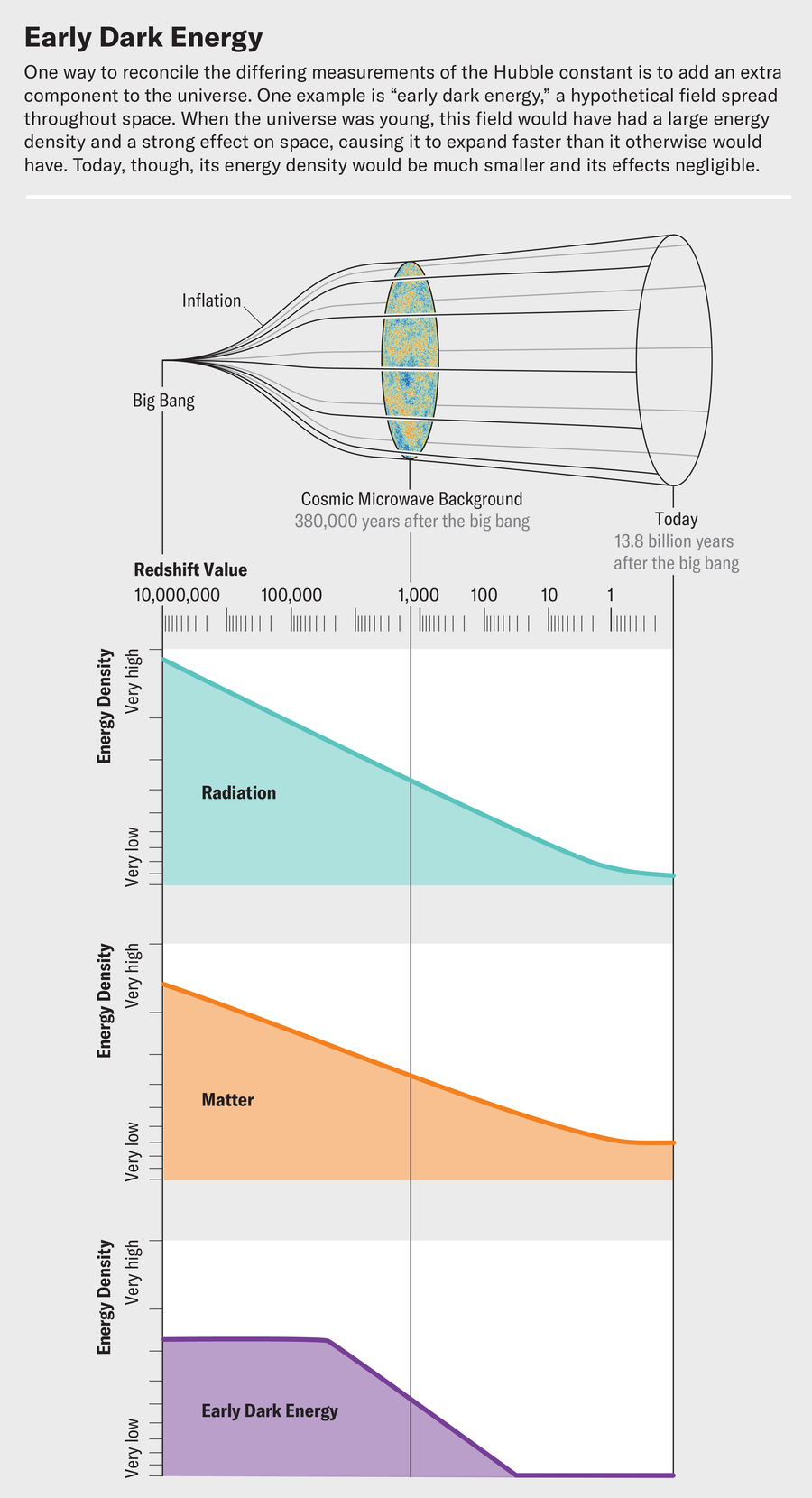
The 2 of us have been deeply concerned on this saga. One (Riess) is an observer and co-discoverer of darkish vitality, one of many final items of the usual cosmological mannequin. He has additionally spearheaded efforts to find out the Hubble fixed by observing the native universe. The opposite (Kamionkowski) is a theorist who helped to determine learn how to calculate the Hubble fixed by measuring the CMB. Extra not too long ago he helped to develop probably the most promising concepts to elucidate the discrepancy—a notion referred to as early darkish vitality.
One risk is that the Hubble rigidity is telling us the newborn universe was increasing quicker than we predict. Early darkish vitality posits that this additional enlargement might need resulted from a further repulsive pressure that was pushing towards area on the time and has since died out.
This suggestion is lastly going through real-world checks, as experiments are simply now changing into able to measuring the sorts of indicators early darkish vitality might need produced. Up to now the outcomes are combined. However as new knowledge are available in over the subsequent few years, we should always be taught extra about whether or not the enlargement of the cosmos is diverging from our predictions and presumably why.
The concept that the universe is increasing in any respect got here as a shock in 1929, when Edwin Hubble used the Mount Wilson Observatory close to Pasadena, Calif., to indicate that galaxies are all shifting aside from each other. On the time many scientists, together with Albert Einstein, favored the thought of a static universe. However the separating galaxies confirmed that area is swelling ever bigger.
In case you take an increasing universe and mentally rewind it, you attain the conclusion that at some finite time up to now, all of the matter in area would have been on prime of itself—the second of the massive bang. The quicker the speed of enlargement, the shorter the time between that large bang and as we speak. Hubble used this logic to make the primary calculation of the Hubble fixed, however his preliminary estimate was so excessive that it implied the universe was youthful than the photo voltaic system. This was the very first “Hubble tension,” which was later resolved when German astronomer Walter Baade found that the distant galaxies Hubble used for his estimate contained totally different sorts of stars than the close by ones he used to calibrate his numbers.
A second Hubble rigidity appeared within the Nineteen Nineties because of sharpening observations from the Hubble House Telescope. The observatory’s measured worth of the Hubble fixed implied that the universe’s oldest stars have been older than stellar-evolution theories instructed. This rigidity was resolved in 1998 with the invention that the enlargement of the cosmos was accelerating. This surprising revelation led scientists so as to add darkish vitality—the vitality of empty area—to the usual mannequin of cosmology. As soon as researchers understood that the universe is increasing quicker now than it did when it was younger, they realized it needed to be a number of billion years older than beforehand thought.
One doable clarification is that the Hubble rigidity is telling us the newborn universe was increasing quicker than we predict.
Since then, our understanding of the origin and evolution of the universe has modified significantly. We will now measure the CMB—our single biggest piece of proof about cosmic historical past—with a precision unimaginable on the flip of the millennium. We’ve got mapped the distribution of galaxies over cosmic volumes tons of of occasions bigger than we had then. Likewise, the variety of supernovae getting used to measure the enlargement historical past has reached a number of thousand.
But our estimates of how briskly area is rising nonetheless disagree. For greater than a decade more and more exact measurements of the Hubble fixed primarily based on the native universe, made regardless of the usual mannequin and due to this fact instantly testing its accuracy, have converged round 73 kilometers per second per megaparsec (km/s/Mpc) of area, plus or minus 1. This determine is simply too massive, and its estimated uncertainty too small, to be suitable with the worth the usual mannequin predicts primarily based on CMB knowledge: 67.5 ± 0.5 km/s/Mpc.
The native measurements are largely primarily based on observations of supernovae in a sure class, kind Ia, that each one explode with an identical vitality output, which means all of them have the identical intrinsic brightness, or luminosity. Their obvious luminosity (how vibrant they seem within the sky) is a proxy for his or her distance from Earth. And evaluating their distance with their pace—which we get by measuring their redshift (how a lot their mild has been shifted towards the purple finish of the electromagnetic spectrum)—tells us how briskly area is increasing.
Astronomers calibrate their kind Ia supernova distance measurements by evaluating them with values for close by galaxies that host each a supernova of this kind and a minimum of one Cepheid variable star—a pulsating supergiant that flares on a timescale tightly correlated to its luminosity, a truth found a century in the past by Henrietta Swan Leavitt. Scientists in flip calibrate this period-luminosity relation by observing Cepheids in very close by galaxies whose distances we will measure geometrically via a way referred to as parallax. This step-by-step calibration is named a distance ladder.
Twenty-five years in the past a landmark measurement of this sort got here out of the Hubble Key Mission, leading to a Hubble fixed measurement of H0 = 72 ± 8 km/s/Mpc. A few dozen years in the past this worth improved to 74 ± 2.5 km/s/Mpc, due to work by two unbiased teams (the SH0ES crew, led by Riess, and the Carnegie Hubble Program, led by Wendy L. Freedman of the College of Chicago). Up to now few years these measurements have been replicated by many research and additional refined with assistance from the European House Company Gaia parallax observatory to 73 ± 1. Even when we exchange a few of the steps within the parallax-Cepheid-supernova calibration sequence with different estimates of stellar distances, the Hubble fixed adjustments little and can’t be introduced beneath about 70 km/s/Mpc with out uncomfortable contrivances or jettisoning many of the Hubble House Telescope knowledge. Even this lowest worth, although, is way too massive in contrast with the quantity inferred from the CMB to be chalked as much as unhealthy luck.
Astronomers have labored via an extended listing of doable issues with the supernova distances and instructed many follow-up checks, however none have revealed a flaw within the measurements. Till not too long ago, one of many remaining issues concerned how we decide Cepheid brightness in crowded fields of view. With the Hubble House Telescope, a few of the mild from any given Cepheid star overlapped with mild from different stars near it, so scientists had to make use of statistics to estimate how vibrant the Cepheid was alone. Just lately, nonetheless, JWST allowed us to reimage a few of these Cepheids with dramatically improved decision. With JWST, the celebrities are very cleanly separated with no overlap, and the brand new measurements are totally in keeping with these from Hubble.
The tactic for inferring the Hubble fixed from the CMB is a little more concerned however relies on related ideas. The depth of the CMB mild could be very practically the identical in every single place in area. Exact measurements present, nonetheless, that the depth varies from one level to a different by roughly one half in 100,000. To the attention, this sample of depth variations seems pretty random. But if we have a look at two factors which are separated by round one diploma (about two full moons aspect by aspect on the sky), we see a correlation: their intensities (temperatures) are more likely to be related. This sample is a consequence of how sound unfold within the early universe.
Throughout the first roughly 380,000 years after the massive bang, area was crammed with a plasma of free protons, electrons and lightweight. At round 380,000 years, although, the cosmos cooled sufficient that electrons might mix with protons to type impartial hydrogen atoms for the primary time. Earlier than then electrons had zoomed freely via area, and lightweight couldn’t journey far with out hitting one. Afterward the electrons have been certain up in atoms, and lightweight might move freely. That preliminary launch of sunshine is what we observe because the CMB as we speak.
Jen Christiansen (graphic), ESA and the Planck Collaboration; NASA/WMAP Science Workforce (CMB photographs); Supply: “A Tale of Many H0,” by Licia Verde et al., arXiv preprint; November 22, 2023 (Hubble fixed knowledge)
Throughout these first 380,000 years, small adjustments within the density of the electron-proton-light plasma that stuffed area unfold as sound waves, simply as sound propagates via the air in a room. The exact origin of those sound waves has to do with quantum fluctuations throughout the very early universe, however we consider them as noise left over from the massive bang. A cosmological sound wave travels a distance decided by the pace of sound in a medium multiplied by the point because the large bang; we name this distance the sound horizon. If there occurred to be a very “loud” spot someplace within the universe on the large bang, then it can finally be “heard” at any level that may be a sound horizon away. When the CMB mild was launched at 380,000 years, it was imprinted with the depth of the soundscape at that time. The one-degree scale correlation within the CMB depth thus corresponds to the angular dimension of the sound horizon at the moment.
That scale is decided by the ratio of the sound horizon to the gap to the “surface of last scatter”—primarily, how far mild has traveled because it was freed when the CMB was launched (the second electrons have been all certain up in atoms, and lightweight might journey freely for the primary time). If the enlargement price of the universe is bigger, then that distance is smaller, and vice versa.
Astronomers can due to this fact use the measurement of the sound horizon to foretell the present price of the universe’s enlargement—the Hubble fixed. The usual mannequin of cosmology predicts a bodily size for the sound horizon primarily based on the gravitationally attracting substances of the early universe: darkish matter, darkish vitality, neutrinos, photons and atoms. By evaluating this size with the measured angular size of the horizon from the CMB (one diploma), scientists can infer a price for the Hubble fixed. The one drawback is that this CMB-inferred worth is smaller, by about 9 %, than the quantity we get hold of by utilizing supernovae.
Hadvert the CMB-inferred worth turned out to be bigger than the native worth, we might have had a reasonably apparent clarification. The gap to the floor of final scatter additionally relies on the character of darkish vitality. If the darkish vitality density isn’t exactly fixed however decreases slowly with time (as some fashions, equivalent to one referred to as quintessence, suggest), then the gap to the floor of final scatter will probably be decreased, bringing the CMB-based worth of the Hubble fixed all the way down to the worth noticed regionally.
Conversely, if the darkish vitality density have been slowly growing with time, then we might infer from the CMB a bigger Hubble fixed, and there can be no rigidity with the supernova measurements. But this clarification requires that vitality by some means be created out of nothing—a violation of vitality conservation, which is a sacred precept in physics. Even when we’re perverse sufficient to think about fashions that don’t respect vitality conservation, we nonetheless can’t appear to resolve the Hubble rigidity. The explanation has to do with galaxy surveys. The distribution of galaxies within the universe as we speak developed from the distribution of matter within the early cosmos and thus reveals the identical sound-horizon bump in its correlations. The angular scale of that correlation additionally permits us to deduce distances to the identical varieties of galaxies that host supernovae, and these distances (utilizing the identical sound horizon as employed for the CMB) give us a low worth of the Hubble fixed, in keeping with the CMB.
Jen Christiansen (graphic), ESA and the Planck Collaboration (CMB picture)
We’re left to conclude that “late-time” options for the Hubble rigidity—those who try to change the relation between the Hubble fixed and the gap to the CMB floor of final scattering—don’t work or a minimum of are usually not the entire story. The choice, then, is to surmise that there could also be one thing lacking in our understanding of the early universe that results in a smaller sound horizon. Early darkish vitality is one risk.
Kamionkowski and his then graduate scholar Tanvi Karwal have been the primary to discover this concept in 2016. The enlargement price within the early universe is decided by the density of all of the matter within the cosmos on the time. In the usual cosmological mannequin, this contains photons, darkish vitality, darkish matter, neutrinos, protons, electrons and helium nuclei. However what if there have been some new part of matter—early darkish vitality—that had a density roughly 10 % of the worth for all the pieces else on the time after which later decayed away?
The obvious type for early darkish vitality to take is a subject, just like an electromagnetic subject, that fills area. This subject would have added a negative-pressure vitality density to area when the universe was younger, with the impact of pushing towards gravity and propelling area towards a quicker enlargement. There are two varieties of fields that might match the invoice. The best possibility is what’s referred to as a slowly rolling scalar subject. This subject would begin off with its vitality density within the type of potential vitality—image it resting on prime of a hill. Over time the sector would roll down the hill, and its potential vitality can be transformed to kinetic vitality. Kinetic vitality wouldn’t have an effect on the universe’s enlargement the way in which the potential vitality did, so its results wouldn’t be observable as time went on.
A second possibility is for the early darkish vitality subject to oscillate quickly. This subject would shortly transfer from potential to kinetic vitality and again once more, as if the sector have been rolling down a hill, right into a valley, up one other hill after which again down once more time and again. If the beginning potential is chosen accurately, then the typical results in an total vitality density with extra potential vitality than kinetic vitality—in different phrases, a scenario that produces unfavourable strain towards the universe (as darkish vitality does) fairly than constructive strain (as bizarre matter does). This extra difficult oscillating situation isn’t required, however it may possibly result in a wide range of attention-grabbing bodily penalties. As an illustration, an oscillating early darkish vitality subject may give rise to particles that might be new darkish matter candidates or may present further seeds for the expansion of a big cosmic construction that might present up within the later universe.
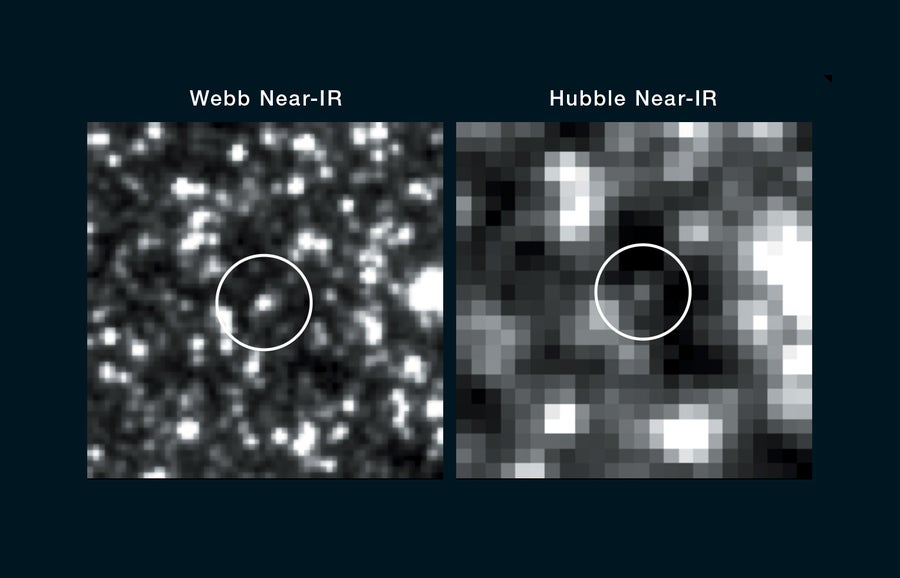

Facet-by-side pictures of a Cepheid star in NGC 5468, a galaxy on the far finish of the Hubble House Telescope’s vary, as taken by the James Webb House Telescope (JWST) and the Hubble, present how a lot sharper the brand new observatory’s imaging is. The JWST knowledge confirmed that distance measurements from Hubble have been correct, regardless of the blurring of Cepheids with surrounding stars within the Hubble knowledge.
NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, Adam G. Riess/ JHU, STScI
After their preliminary suggestion of early darkish vitality in 2016, Kamionkowski and Karwal, together with Vivian Poulin of the French Nationwide Middle for Scientific Analysis (CNRS) and Tristan L. Smith of Swarthmore School, developed instruments to check the mannequin’s predictions with CMB knowledge. It’s laborious to depart a lot from the usual cosmological mannequin when we now have such exact measurements of the CMB that to date match the mannequin very properly. We figured it was an extended shot that early darkish vitality would really work. To our shock, although, the evaluation recognized courses of fashions that will enable a better Hubble fixed and nonetheless match the CMB knowledge properly.
This promising begin led others to create a proliferation of variants of early darkish vitality fashions. In 2018 these fashions fared about in addition to the usual mannequin in matching CMB measurements. However by 2021 new, higher-resolution CMB knowledge from the Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT) appeared to favor early darkish vitality over the usual mannequin, which drew much more scientists towards the thought. Up to now three years, nonetheless, extra measurements and evaluation from ACT, in addition to from the South Pole Telescope, the Darkish Vitality Survey and the Darkish Vitality Spectroscopic Instrument, led to extra nuanced conclusions. Though some analyses maintain early darkish vitality within the working, many of the outcomes appear to be converging towards the usual cosmological mannequin. Even so, the jury remains to be out: a broad array of possible early darkish vitality fashions stay viable.
Many theorists assume it might be time to discover different concepts. The issue is that there aren’t any significantly compelling new concepts that appear viable. We’d like one thing that may improve the enlargement of the younger universe and shrink the sound horizon to lift the Hubble fixed. Maybe protons and electrons by some means mixed otherwise to type atoms at the moment than they do now, or perhaps we’re lacking some results of early magnetic fields, humorous darkish matter properties or subtleties within the preliminary circumstances of the early universe. Cosmologists will agree that straightforward explanations proceed to elude us even because the Hubble rigidity turns into extra firmly embedded within the knowledge.
To progress, we should proceed to search out methods to scrutinize, examine and check each native and CMB-inferred values of the Hubble fixed. Astronomers are creating methods for gauging native distances to reinforce the supernova-based approaches. Measurements of distances to quasars primarily based on radio-interferometric methods, for example, are advancing, and there are prospects for utilizing fluctuations in galaxy-surface brightness. Others try to make use of kind II supernovae and totally different sorts of purple large stars to measure distances. There are even proposals to make use of gravitational-wave indicators from merging black holes and neutron stars. We’re additionally intrigued by the potential to find out cosmic distances with gravitational lensing.
Though present outcomes are usually not but exact sufficient to weigh in on the Hubble rigidity, we count on to see nice progress when the Vera C. Rubin Observatory and the Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope come on-line. For now we now have no good solutions, however numerous nice questions and experiments are underway.

