This text is a part of “Innovations In: Sickle Cell Disease,” an editorially unbiased particular report that was produced with monetary help from Vertex Prescription drugs.
Sickle cell illness might sound easy sufficient: it’s brought on by a single mutation in a single gene. However the best way it impacts sufferers is remarkably complicated—so complicated that 70 years after that mutation was found, therapy stays tough. In folks with wholesome crimson blood cells, hemoglobin proteins carry oxygen because the cells flow into all through the physique. In sufferers with sickle cell, the namesake cells type when mutant hemoglobin proteins clump collectively into fibers, deforming crimson blood cells’ regular saucer form right into a curved sickle, which prevents them from successfully delivering oxygen to tissues. These sickle cells can get caught inside blood vessels, interrupting blood move and sometimes prompting intense ache and a disaster so extreme it sends folks to the hospital and places them vulnerable to cardiac failure and different life-threatening points. Over the long run, disrupted blood move, oxidative stress and irritation mix to trigger strokes and everlasting injury to blood vessels and different organs.
The illness strikes in so many ways in which researchers are attacking the issue from a number of angles: on the supply by stopping bone marrow from producing mutant crimson blood cells within the first place; on the mobile stage by modifying the misshapen crimson blood cells’ metabolism and protein construction; and on the immune stage to stop long-term organ injury. “The problem is [it’s] all connected,” says Marilyn Telen, a hematologist at Duke College. “So where do you build the dam?”
On supporting science journalism
For those who’re having fun with this text, take into account supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world at the moment.
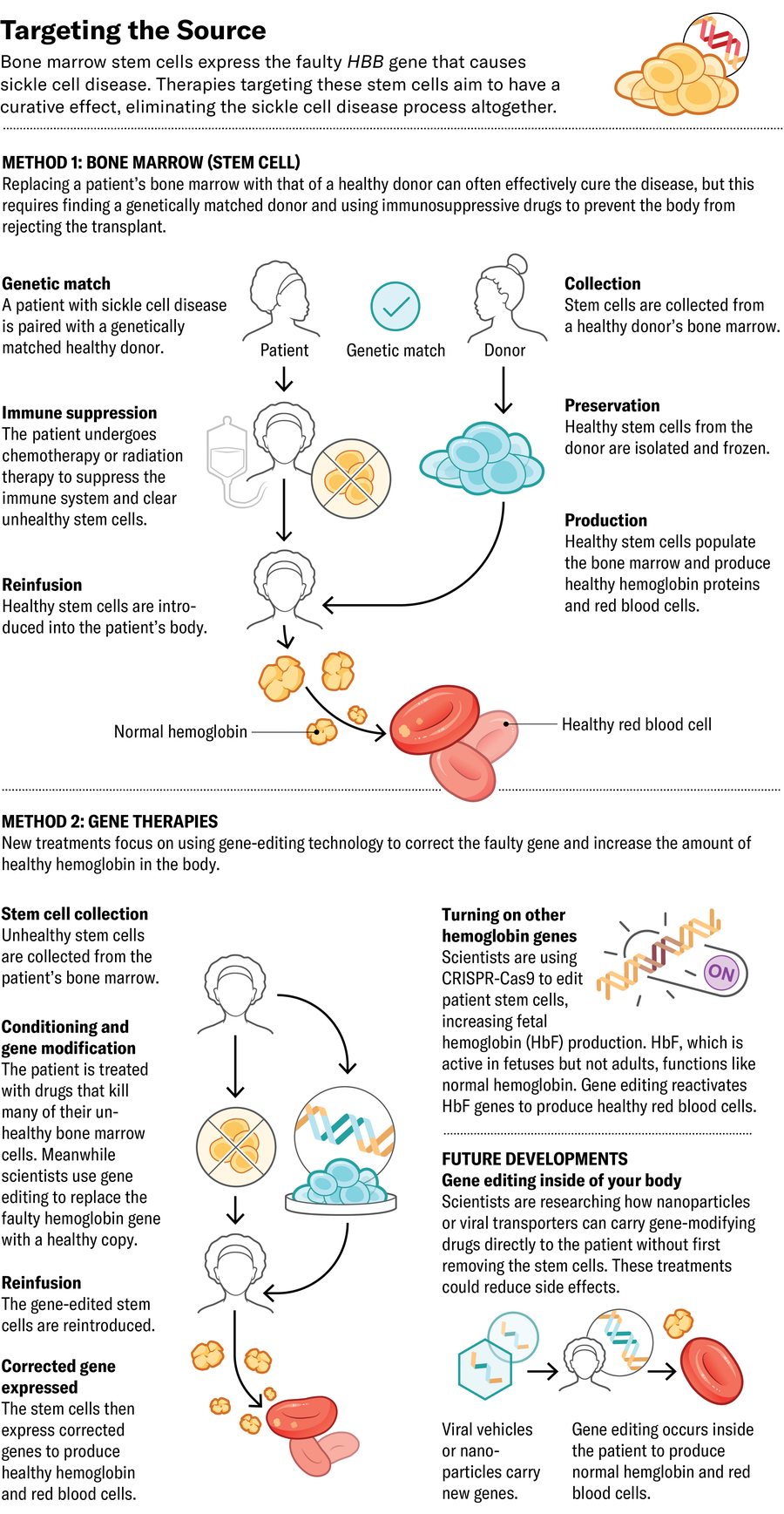
The perfect place to halt the illness is at its supply: if bone marrow stem cells are producing the defective crimson blood cells, change them with ones that produce wholesome cells. Essentially the most established technique for this method is a bone marrow transplant from a matched donor. The process requires eliminating the affected person’s authentic bone marrow cells pretransplant, utilizing a course of robust chemotherapy, to create a distinct segment for the launched cells to develop in. The therapy could cause infertility and necessitates an extended course of immunosuppressive medicine—usually continued for years—to stop the physique from rejecting its transplant.
Now Medical Studios; Supply: Kelly Rose, chief scientific officer at American Society of Hematology (marketing consultant)
To attempt to enhance on the success of bone marrow transplants, some firms have created gene-editing approaches that get rid of the necessity for immunosuppressive medicine. They take away sufferers’ stem cells, modify the cells’ DNA in a laboratory to immediate the manufacturing of wholesome hemoglobin, then reintroduce them to the affected person. Plenty of these gene-modifying approaches have already made their technique to scientific trials or been authorized by the U.S. Meals and Drug Administration.
The type of hemoglobin that infants make at start, referred to as fetal hemoglobin (HbF), isn’t affected by the sickle mutation. Usually HbF is usually changed by the grownup model of hemoglobin inside just a few months after start, main a number of firms to concentrate on growing the quantity of HbF within the bloodstream. In 2023 the FDA authorized Vertex Prescription drugs’s exa-cel, which makes use of CRISPR-Cas9 gene enhancing to deactivate the gene that forestalls manufacturing of HbF. The result’s a better fetal-to-adult hemoglobin ratio.
Editas Medication can also be enhancing HbF manufacturing, utilizing a unique CRISPR-related enzyme referred to as Cas12a to do the enhancing. Whereas Cas9 edits DNA by breaking each strands of the double helix in the identical place, Cas12a breaks them at totally different positions and ends in extra constant edits. Beam Therapeutics is pursuing an analogous technique, utilizing one other type of CRISPR to swap single nucleotides within the genetic code that improve HbF manufacturing. Each therapies are nonetheless in scientific trials.
Now Medical Studios; Supply: Kelly Rose, chief scientific officer at American Society of Hematology (marketing consultant)
A distinct technique is to insert a extra resilient model of the gene encoding grownup hemoglobin quite than growing HbF. Bluebird bio’s lovo-cel, which additionally acquired FDA approval final 12 months, makes use of a extra classical gene remedy method. Slightly than enhancing a affected person’s DNA, it makes use of a modified virus to ship a wholesome, enhanced copy of the grownup hemoglobin gene into bone marrow stem cells, the place it integrates into the affected person’s DNA.
These new applied sciences, says Alexis Thompson, a pediatric hematologist at Kids’s Hospital of Philadelphia, are “an improvement over the many years and decades when we had very little to offer families.”
A future method would possibly let medical doctors edit sufferers’ bone marrow with out eradicating it from the physique. In a examine printed final 12 months in Science, researchers described the event of nanoparticles that carry messenger RNA (mRNA) into stem cells within the bone marrow. Once they used the particles in cells from folks with sickle cell illness, the enhancing system encoded by the mRNA efficiently modified the hemoglobin gene in these cells’ genomes to supply extra wholesome hemoglobin protein.
It might be as many as 10 to twenty years earlier than such in vivo expertise is prepared for large-scale human trials, Telen says. “We know the technology we need. We know a lot of the pieces. We just haven’t been able to get it to all work together.”
Within the meantime present gene therapies stay costly and difficult to scale up as a result of every affected person’s batch of cells must be edited individually. The therapies are out of attain for most individuals with the illness, notably in sub-Saharan Africa, the place 75 p.c of all sickle cell instances happen.
Now Medical Studios; Supply: Kelly Rose, chief scientific officer at American Society of Hematology (marketing consultant)
All of because of this, for most individuals, essentially the most accessible healing therapy is bone marrow transplantation from a donor with particular, genetically matched mobile markers. (Such matches are sometimes however not all the time discovered amongst shut relations.) And now a method initially developed for treating blood cancers may make extra transplants doable by increasing the donor pool. A technique that features a temporary course of two chemotherapy medicine—thiotepa and cyclophosphamide—suppresses the immune programs of bone marrow recipients sufficient to permit them to obtain transplants from nearly any donor who shares half of their DNA, corresponding to a father or mother, cousin or sibling with out sickle cell illness.
In a 54-person trial, researchers discovered that round 90 p.c of sickle cell sufferers handled with this system who acquired transplants from half-matched donors went at the very least two years with out rejection. Some sufferers appeared utterly cured, says hematologist Adetola Kassim of Vanderbilt College, who led the examine. And in contrast to gene remedy, this “haploidentical transplant” requires solely a short and much much less poisonous course of chemotherapy. Kassim says this method could also be a extra inexpensive choice: “The technique we use is exportable and scalable.”
When bone marrow transplants are out of attain, therapies that act additional downstream can tackle physiological points, corresponding to hemoglobin clumping, and ameliorate signs. “The argument could be made that the vast majority of sickle cell patients in the world are unlikely to get curative treatment,” Telen says. “So it behooves us to bring other drugs onto the market to improve their lives.”
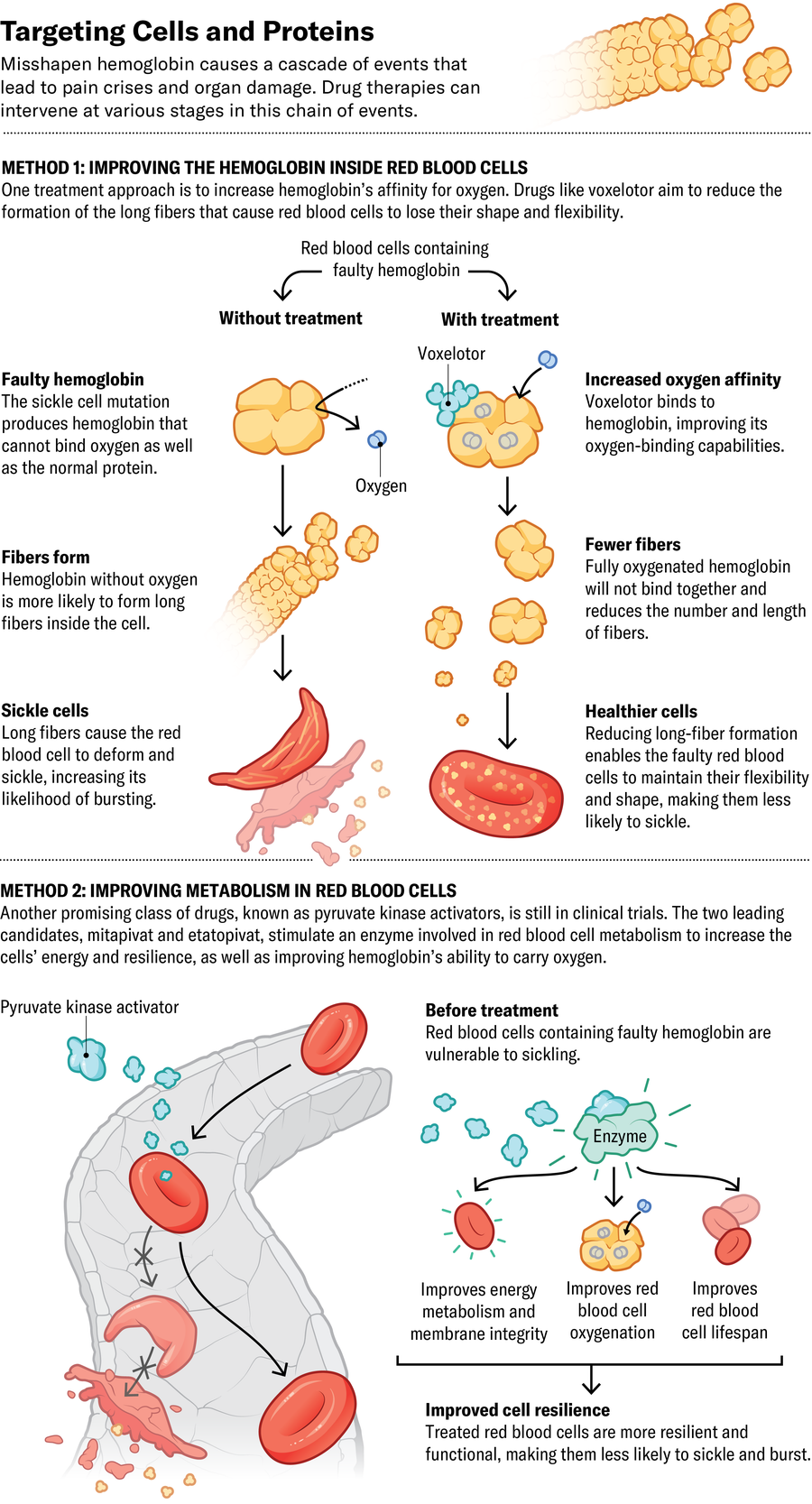
The FDA has authorized three sickle cell medicine in recent times, and dozens extra are within the pipeline. The primary new drug, authorized in 2017, was Emmaus Medication’s l-glutamine, an antioxidant that helps to take care of crimson blood cells’ spherical form. In a scientific trial, sufferers consuming l-glutamine powder blended into meals or drinks had 25 p.c fewer ache crises than these within the placebo group.
Pfizer’s voxelotor and osivelotor, the latter of which is in scientific trials, each bind on to hemoglobin and enhance its potential to hold on to oxygen. This motion additionally prevents the protein from clumping and inflicting crimson blood cells to lose their form. The FDA and European Fee authorized voxelotor in 2019 and 2022, respectively, after information confirmed it may elevate hemoglobin ranges and shield towards extreme anemia. “When it works, it’s amazing. It’s somewhat of a miracle drug,” says Jeffrey Glassberg, an emergency medication doctor specializing in sickle cell on the Icahn College of Medication at Mount Sinai in New York Metropolis. However some sufferers don’t reply, and a section 3 scientific trial suggests it doesn’t scale back the variety of ache crises.
Now Medical Studios; Supply: Kelly Rose, chief scientific officer at American Society of Hematology (marketing consultant)
One other promising class of medicine, often known as pyruvate kinase activators, stimulate an enzyme concerned in mobile metabolism to each enhance cells’ power and enhance hemoglobin’s potential to hold oxygen. The 2 main candidates, Agios Prescription drugs’s mitapivat and Novo Nordisk’s etavopivat, are in scientific trials.
Physicians nonetheless have few decisions for serving to somebody within the throes of an assault. Usually the one out there choices are ache medicine and intravenous fluids. However new medicine that focus on one thing apart from crimson blood cells would possibly assist with acute crises and scale back the immune reactions that contribute to ache and organ injury over time.
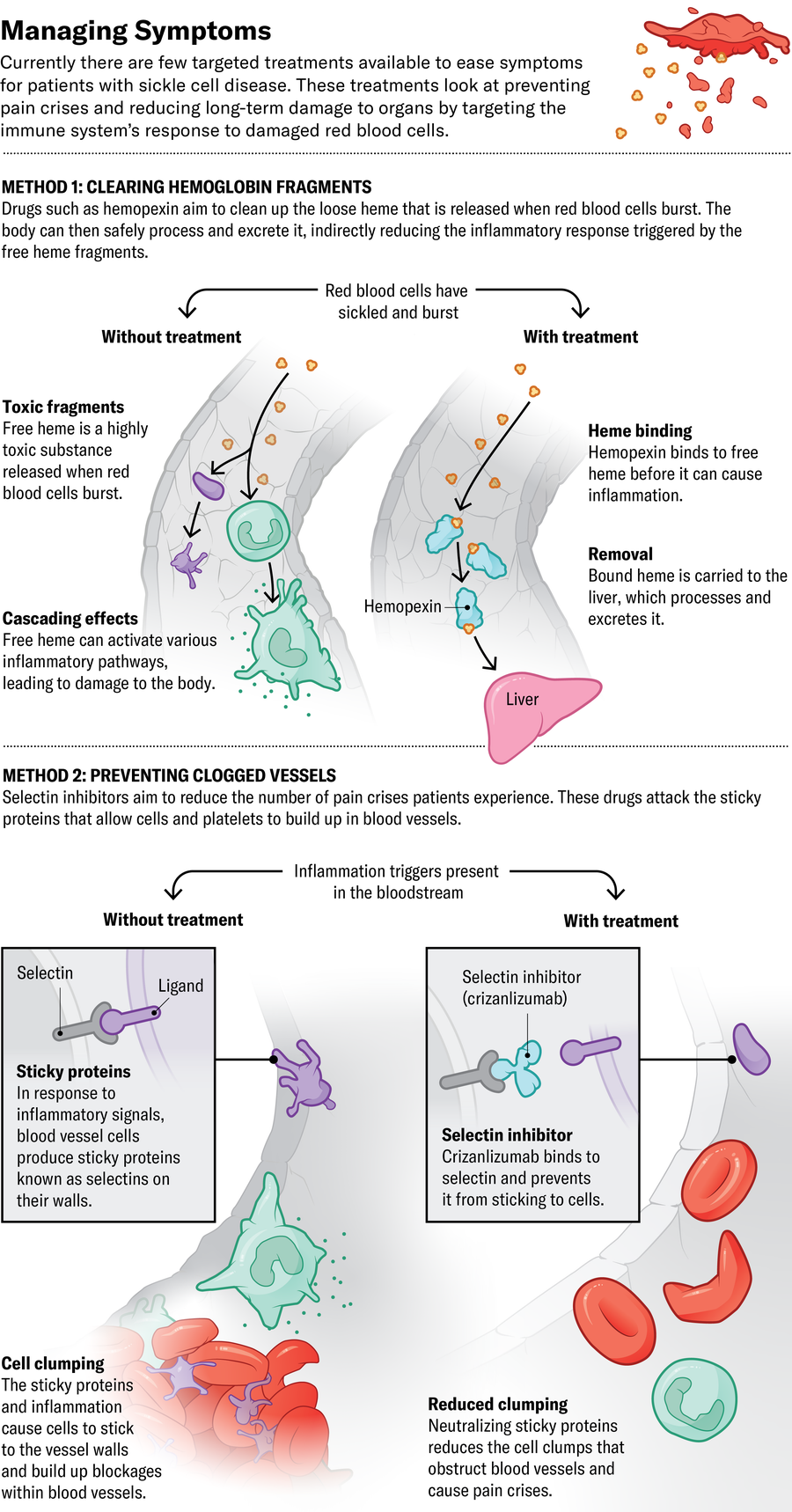
The third drug just lately authorized by the FDA, Novartis’s crizanlizumab, assaults sticky proteins referred to as selectins on blood vessels and platelet cells. Blocking these proteins prevents crimson blood cells from clumping collectively contained in the vessels, supposedly stopping ache crises. Nevertheless it is probably not fairly that easy. The European Medicines Company revoked its approval of crizanlizumab in 2023 after a assessment committee discovered it didn’t appear to cut back the variety of crises folks skilled. Glassberg thinks the drug remains to be helpful—his unpublished analysis means that crizanlizumab and related medicine presently in scientific trials may scale back long-term organ injury and persistent kidney illness.
Different approaches goal to decrease immune system exercise. CSL Behring is conducting scientific trials of hemopexin, a drug that cleans up hemoglobin that has damaged freed from crimson blood cells. Free hemoglobin causes cells to clump in blood vessels and contributes to irritation, resulting in long-term organ injury. Researchers elsewhere are investigating whether or not tamping the exercise of sure immune-signaling molecules often known as complement proteins would possibly stop the identical inflammation-based damage.
Now Glassberg and others try to find out which of those medicine work greatest and whether or not sure combos would possibly work synergistically. He’s presently working a trial at Mount Sinai referred to as REAL Solutions, through which 1,200 sufferers will obtain the newly FDA-approved medicine, in addition to an older one referred to as hydroxyurea, alone or in combos. Glassberg’s group is assessing their results on ache crises, monitoring for indicators of organ damage and looking for genetic markers that might predict how nicely somebody will reply.
It’s too quickly to know the way most of those new therapies will match into affected person care. They may be handiest when began early in life. The medicine haven’t but been extensively examined for security and efficacy in kids, however such an method would possibly stop organ injury that may begin early after which worsen over time.

