The fossilized stays of a brand new horned dinosaur have simply been found within the mountains of Montana. And it is a big.
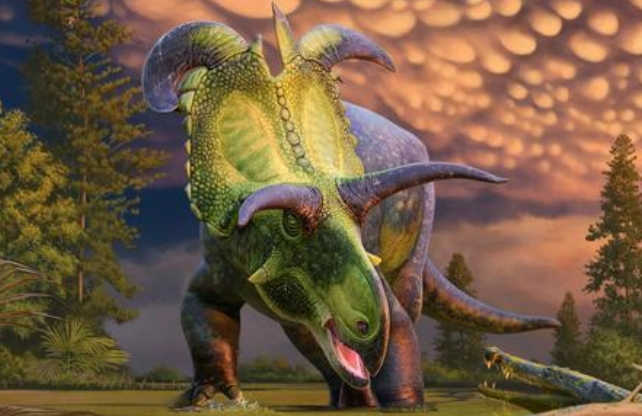
Lokiceratops rangiformis is without doubt one of the largest ceratopsian dinosaurs to have ever roamed our planet, belonging to a household of horned beasts that features Triceratops and Styracosaurus.
What’s extra, the 2 lengthy, curving horns that adorned the crest of its cranium are probably the most astonishing ever documented. It is for these horns that the dinosaur will get its identify, from the spectacular helmet worn by the Marvel character Loki.
Lokiceratops lived 78 million years in the past, alongside a number of different frilled dinos of the Centrosaurine subfamily in what was as soon as the Cretaceous island continent of Laramidia, however it was bigger and heavier than all of them.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
Though the bones are all from only a single particular person, by an enormous stroke of luck they make up a lot of the dinosaur’s cranium.
From this, we all know that Lokiceratops had horns in contrast to another, topped by the 2 massive, caribou-like uneven horns on the highest of the frill – the big, shield-like bony plate present in ceratopsians. It additionally lacked the nostril horn typical in different beasts of its ilk.
“This new dinosaur pushes the envelope on bizarre ceratopsian headgear, sporting the largest frill horns ever seen in a ceratopsian,” says paleontologist Joseph Sertich of the Smithsonian Tropical Analysis Institute. The paleontologists imagine the dinosaurs used their horns very like birds use their totally different feathers, for mate choice or species recognition.
“These skull ornaments are one of the keys to unlocking horned dinosaur diversity and demonstrate that evolutionary selection for showy displays contributed to the dizzying richness of Cretaceous ecosystems.”
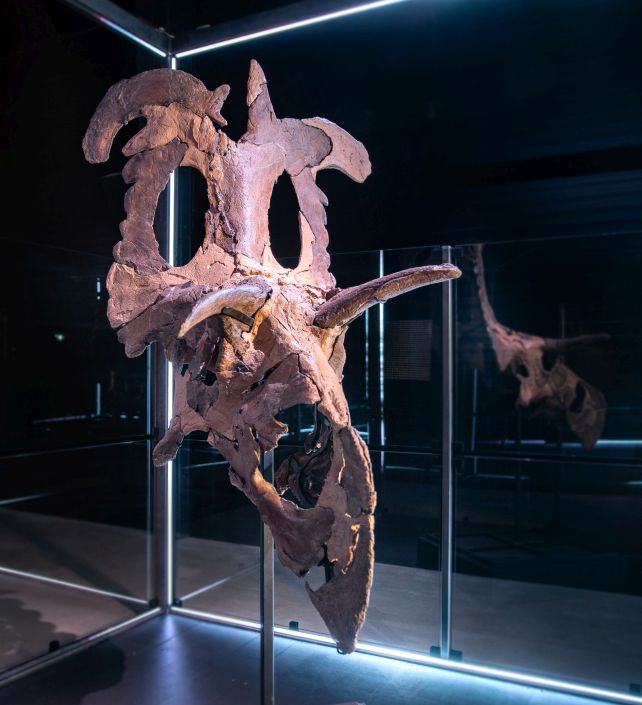

The fossilized bones have been discovered within the Judith River Formation in Montana, a fossil deposit from which the bones of 4 different dinosaurs have been retrieved.
However, when Sertich and his colleague, paleontologist Mark Loewen of the College of Utah, began reconstructing the cranium from bones excavated in 2019, they realized they have been taking a look at one thing no person had ever seen earlier than.
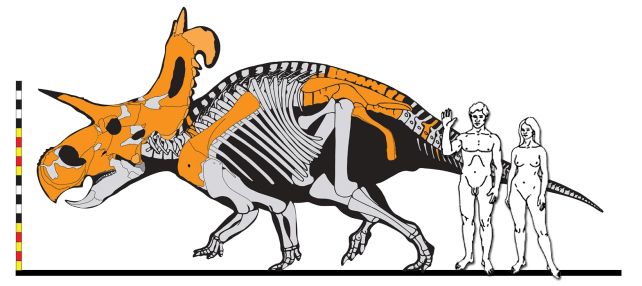
And it was, dare we are saying, a chonker.
Lokiceratops is estimated to have measured some 6.7 meters (22 ft) in size, with a cranium greater than 2 meters lengthy from nostril to horn-tips. And it might have tipped the scales at round 5 metric tons (11,000 kilos). That places it on a par with the largest elephants discovered on Earth at present.
It is nonetheless not fairly as huge as Triceratops, which got here alongside round 10 million years later in Earth’s historical past, however you’d nonetheless need to get out of its manner if it was charging at you, head lowered.

One other attention-grabbing factor about Lokiceratops is the opposite dinosaurs within the formation during which its stays have been discovered.
Three of the opposite species are additionally Centrosaurines, carefully associated to one another and Lokiceratops, and the fourth was one other horned dinosaur. The opposite Centrosaurines are additionally not identified outdoors Laramidia.
“Previously, paleontologists thought a maximum of two species of horned dinosaurs could coexist at the same place and time,” Loewen explains. “Incredibly, we have identified five living together at the same time.”
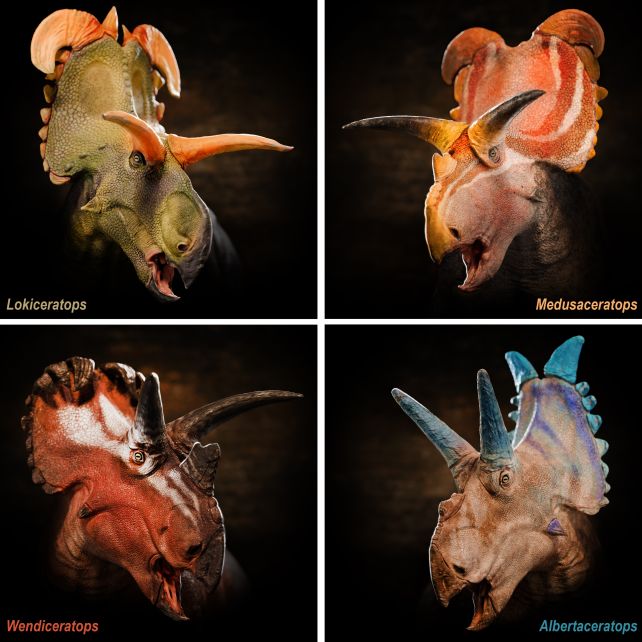
The isolation of ceratopsian dinosaurs on Laramidia is probably going what led to the big sizes and diversification of the animals discovered there, together with the distinctive preparations of horned protuberances on their big heads. This speedy speciation might be present in remoted animal communities, most notably the finches in Galapagos.
This means that we could also be vastly underestimating the range of dinosaurs, the researchers say.
“Rapid evolution may have led to the 100- to 200-thousand-year turnover of individual species of these horned dinosaurs,” Loewen says, including, “Lokiceratops helps us understand that we only are scratching the surface when it comes to the diversity and relationships within the family tree of horned dinosaurs.”
The analysis has been revealed in PeerJ.

